What is Market Making?
마켓메이킹이란 무엇인가요?

이 페이지에 오셨다면, 아마도 다음 질문 중 하나를 해보셨을 가능성이 높습니다:
- 마켓 메이커란 무엇인가요?
- 마켓 메이커는 무슨 일을 하나요?
- 어떻게 마켓 메이커가 될 수 있나요?
- 마켓 메이킹 로봇은 어떻게 만드나요?
- 그렇다면, 제대로 찾아오셨습니다!
저희 Hummingbot의 목표는 여러분이 마켓 메이킹에 대해 더 많이 배우고, 저희의 무료 오픈소스 로봇을 사용하여 자신만의 전략을 구현하는 방법을 돕는 것입니다.
그런데 마켓 메이커가 무엇일까요?
마켓 메이커(MM)는 유가증권 시장에서 매수(bid)와 매도(ask) 호가를 적극적으로 제시하며 양방향 시장을 조성하고, 각 호가의 시장 규모를 함께 제공하는 회사 또는 개인을 말합니다. (출처)
위 인용문이 잘 이해되지 않았다면, 전당포를 상상해 보세요:

수잔은 오래된 기타를 가지고 있지만 더 이상 연주할 시간이 많지 않고, 현금이 좀 필요하다고 가정해 봅시다. 한편, 도시의 다른 곳에서는 마이크가 친구의 기타로 연주를 배우다가 이제 자신의 기타를 살 만큼 실력이 늘었다고 생각하지만, 새 기타는 너무 비쌀 수 있습니다.
거래를 성사시킬 수 있는 두 사람이 있지만, 서로를 찾거나 기타에 대한 합리적인 가격에 합의하기는 어려울 수 있습니다.
바로 이 지점에서 전당포가 등장합니다:
수잔은 기타를 사려는 사람을 찾아다니는 대신, 전당포에 기타를 팔 수 있고, 마이크는 그곳에 가면 기타를 찾을 수 있다는 것을 알고 찾아갈 수 있습니다.
전당포 주인은 수잔과 마이크 모두에게 서비스를 제공하고 있습니다. 그는 그들이 원하는 것을 쉽게 팔거나 살 수 있는 방법(유동성 제공)과, 마을의 중고 기타 수요에 기반한 공정한 가격(스프레드 축소)을 제공합니다.
전당포는 이 서비스의 대가로 수잔에게 지불한 가격과 마이크로부터 받은 가격의 차액(스프레드 크기)으로 수익을 얻습니다.
💡 마켓 메이커는 전당포 주인처럼 금융 시장에서 동일한 종류의 서비스를 제공합니다. 그는 유동성을 공급하고 매수-매도 스프레드 크기를 줄이는 데 도움을 주며, 자신의 매수 주문과 매도 주문 간의 차액(스프레드)에서 이익을 얻습니다.
금융 시장에서 마켓 메이킹은 어떻게 이루어지나요?
금융 시장은 실제 경제의 공개 시장과 크게 다르지 않습니다. 매일 수백만 명의 사람들이 어떤 종류의 거래 플랫폼에 접속하여 주식, 채권, 석유, 금, 계약, 암호화폐 등 다양한 자산에 대한 거래를 체결하고자 합니다.
하지만 수천 명의 사람들이 한 장소에 모여 팻말을 들고 있거나 무언가를 얼마에 사거나 파는지 소리치는 대신, 금융 자산 시장은 모든 매수 및 매도 제안이 한 곳에 집계되는 오더북(order book)을 사용합니다:
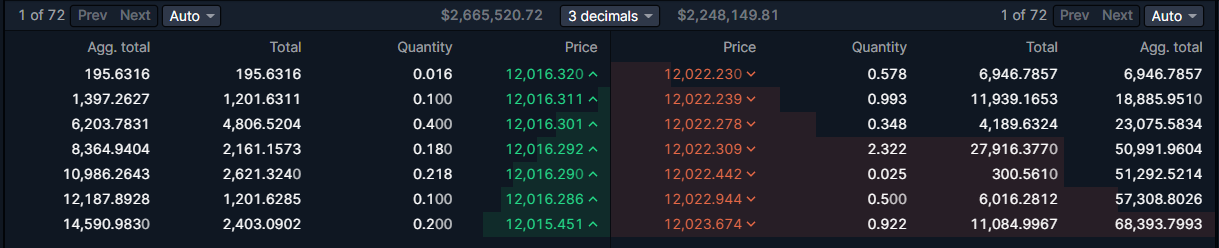
오더북은 모든 시장 참여자들이 제시한 모든 매수 및 매도 제안(수량과 가격 포함)의 목록에 불과합니다.
위 사진에서 우리는 BTC/USD 페어의 오더북을 볼 수 있습니다. 만약 지금 비트코인을 사려는 사람이 있다면, 그는 12,022.230달러(가장 낮은 매도 호가)를 지불해야 하며, 그 가격에는 0.578 BTC가 있습니다.
하지만 즉시 비트코인을 팔고 싶은 사람이 있다면, 그는 최대 0.016 BTC에 대해 12,016.32달러(가장 높은 매수 호가)의 가격을 받아들여야 합니다.
💡 상품이나 자산에 대한 가장 낮은 매도 호가와 가장 높은 매수 호가 사이의 차이를 스프레드(spread)라고 합니다.
기술적으로, 오더북에 매수 또는 매도 제안을 올리는 모든 사람은 마켓 메이커(maker) 역할을 하는 것이며, 오더북에 제시된 가격을 받아들이는 사람들은 마켓 테이커(taker)라고 불립니다.
마켓 메이커로 활동하는 것은 개념적으로 “전당포 주인”처럼 시장에 참여하는 것과 유사합니다. 자산을 낮은 가격에 사겠다는 제안을 만들고, 가능한 한 빨리 그리고 가능한 한 여러 번 더 높은 가격에 파는 것입니다.
💡 가장 일반적인 트레이딩/투자 전략이 큰 가격 변동에서 이익을 얻으려는 반면, 전문 마켓 메이커는 두 가격 수준 사이의 더 작지만 더 일관된 가격 변동을 이용하려고 합니다.
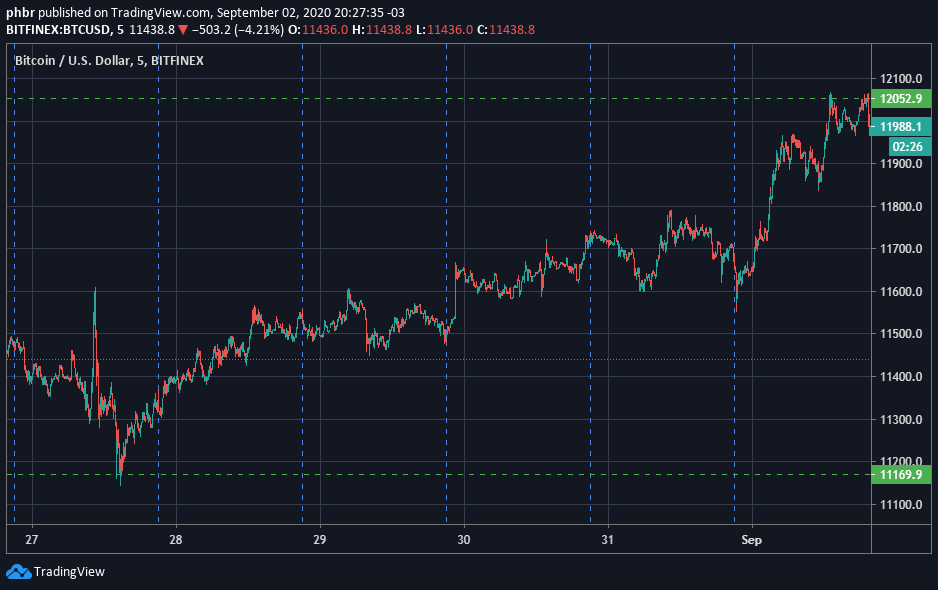
대부분의 트레이더와 투자자들은 시장이 이렇게 움직이는 것을 보고 싶어 합니다:
반면 마켓 메이커들은 시장 가격이 이렇게 움직이는 것을 좋아합니다:
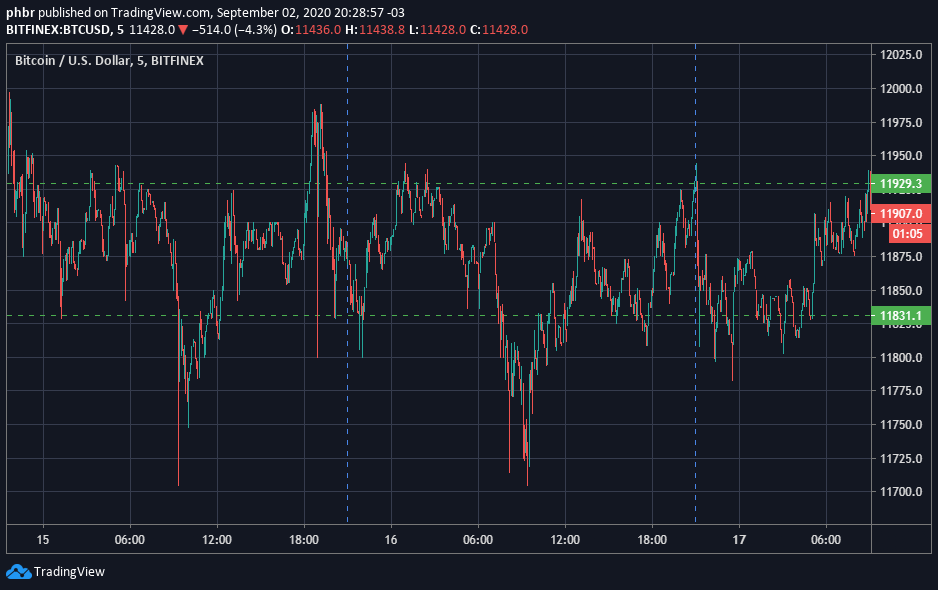
자산의 가격은 일정한 흐름으로 변하는 것이 아니라 파도처럼 변합니다. 트레이더와 투자자들이 바다가 밀물로 향하는지 썰물로 향하는지 알아내려고 하는 동안, 마켓 메이커는 해변의 더 작은 파도를 지켜보고 있습니다.
매수-매도 스프레드 vs 마켓 메이커 스프레드
앞서 본 사진의 오더북 상태를 보면, 마켓 메이커는 두 가지 제안을 올릴 수 있습니다:
- 비트코인 1개를 12,016.320달러에 매수 (매수 호가)
- 비트코인 1개를 12,022.230달러에 매도 (매도 호가)
다른 시장 참여자들이 이 가격들을 받아들여 양쪽 주문이 모두 체결되면, 마켓 메이커는 이 거래에서 5.91달러의 이익을 얻게 됩니다.
이것은 시장의 매수-매도 스프레드로도 알려져 있으며, 위 예시에서는 마켓 메이커가 작업의 양쪽을 모두 완료하여 받은 5.91달러의 이익입니다:
\[\frac{(12,022.23-12,016.32)}{12,016.32} = 0.049\%\]일부 거래소는 실시간으로 매수-매도 스프레드를 시각화하는 방법을 제공하기도 합니다 (오더북에 게시된 모든 주문의 누적 크기인 북 뎁스(book depth)와 함께):
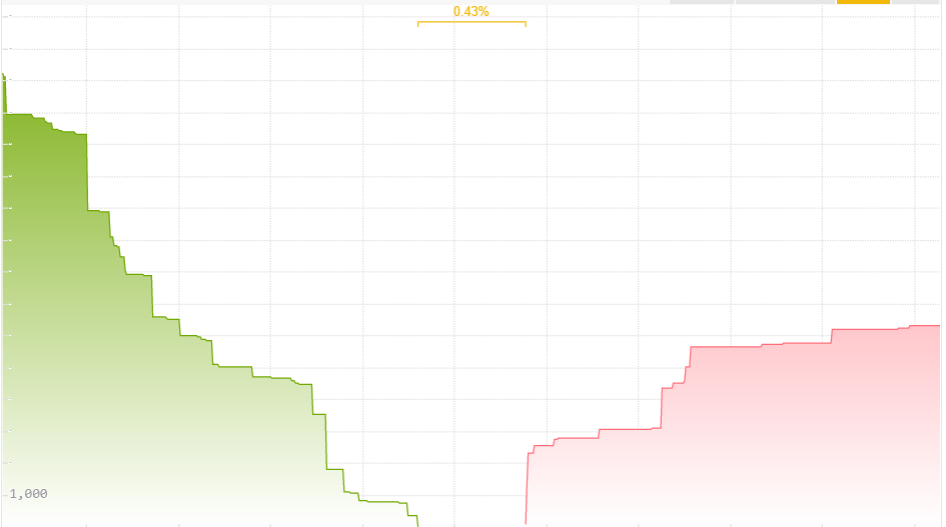
하지만 이것이 마켓 메이커가 항상 이 정확한 매수 및 매도 가격을 사용해야 한다는 의미는 아닙니다.
마켓 메이커는 자신의 운영 스프레드를 결정할 때 다른 요인들을 고려해야 합니다, 예를 들면:
- 시장의 매수-매도 스프레드;
- 거래 비용 (거래소 수수료 및/또는 이체 수수료 포함);
- 거래량;
- 시장 변동성;
- 운영 비용 (전기 요금, 클라우드 서버 비용 등);
- 거래 운영과 관련된 기타 모든 비용.
마켓 메이커 스프레드가 얼마나 커야 하는지 또는 작아야 하는지에 대한 정답은 없으며, 결국 스프레드는 마켓 메이커 전략의 일부일 뿐입니다.
🐦 Hummingbot에서는
config ask_spread명령어로 매도 주문의 스프레드 비율을,config bid_spread명령어로 매수 주문의 스프레드 비율을 변경할 수 있습니다.
전략에는 무엇이 포함되나요?
수익성 있는 마켓 메이커가 되는 것은 단지 스프레드 크기를 선택하고, 오더북에 지정가 주문을 보내기 시작한 다음, 뒤돌아서 잊어버리는 것만이 아닙니다.
마켓 메이킹 운영을 시작하기 전에, 스스로에게 몇 가지 질문을 해야 합니다:
- 스프레드를 항상 고정시켜야 할까? 시장 상황에 따라 변경해야 할까?
- 내 주문의 크기는 얼마로 해야 할까?
- 시장에 가격 추세가 있을 때, 또는 명확한 추세가 없을 때 어떻게 해야 할까?
- 시장 방향은 어떻게 감지할 것인가?
- 내 주문은 오더북에 얼마나 오래 있어야 할까?
- 한쪽 주문이 체결되면, 반대쪽 주문은 체결될 때까지 유지해야 할까?
- 시간이 지남에 따라 한 자산을 더 많이 축적하고 싶은가, 아니면 항상 50/50 잔액을 유지하고 싶은가?
- 가격 급등이 있을 때 어떻게 해야 할까?
- 평균 매수 비용을 신경 써야 할까?
- 언제 시장에서 벗어나야 하고 그 이유는 무엇이며, 아니면 항상 거래해야 할까?
- 무엇을 잃을 수 있고, 얼마나 많은 위험을 감수하고 있는가?
- 이 질문들에 대한 답은 시장 상황에 따른 당신의 행동(그리고 반응)을 결정하며, 궁극적으로 당신의 전략을 정의할 것입니다.
좋은 마켓 메이킹 전략은 시장 변화에 어떻게 반응할지 미리 계획하는 것에 불과합니다.
하지만 이 모든 질문에 겁을 먹고 마켓 메이킹을 포기하기 전에, 여기 팁이 있습니다:
💡 작게 시작하세요. 사전에 전략에 대한 모든 답을 가지려고 하지 말고, 한 번에 하나의 매개변수에 집중하여 다른 시장 상황에서 어떤 일이 일어나는지 테스트하고 관찰하세요. 시간이 지나면 다른 매개변수를 추가하고 더 많은 테스트를 하며 모든 조각들이 함께 어떻게 작동하는지 지켜보세요.
규격화되어 있고, 바로 사용할 수 있으며, 모든 상황에 맞고, 항상 수익성 있는 전략/매개변수를 그냥 찾을 수는 없겠지만, 시간이 지나면 각 전략의 장단점을 이해하기 시작할 것이고, 몇 가지를 실험해 본 후에는 자신의 목표에 맞는 것을 찾게 될 것입니다.
🐦 Hummingbot에서는
config명령어를 사용하여 다양한 설정을 여러 가지 방법으로 조합하여 매우 다양한 전략을 구축할 수 있습니다. 순수 마켓 메이킹(pure market making) 참조 가이드를 확인하여 각 매개변수가 무엇에 사용되는지 알아보세요.
자동화된 트레이딩과 마켓 메이킹
자, 트레이딩 로봇… 아마 당신이 이 글을 읽는 또 다른 이유일 것입니다. 당신은 단지 마켓 메이커가 되려는 것이 아니라, 모든 힘든 일을 해줄 마켓 메이킹 로봇을 설정하려는 것입니다.
결국, Hummingbot은 자동화된 트레이딩 전략을 시작하고자 하는 모든 사람에게 무료로 제공되는 오픈소스 트레이딩 로봇입니다.
수동으로 마켓 메이킹 작업을 하는 것도 가능하지만, 트레이딩 로봇을 사용하면 전략을 정밀하게 실행할 수 있고, 감정적 요인(탐욕과 공포)을 제거하며, 더 나은 위험 관리를 위한 안전 조치를 만들 수도 있습니다.
하지만 모든 로봇이 똑같이 만들어지지는 않았으며, 어떤 종류의 전략을 사용할 것인지(고빈도, 저빈도, 추세 추종, 그리드, 스트래들, 퀀트… 가능성은 매우 많습니다)에 따라 한 로봇이 다른 로봇보다 더 나은 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
결국, 트레이딩 로봇은 도구이며 우리는 작업에 맞는 올바른 도구를 사용해야 합니다.
Hummingbot은 암호화폐 시장을 위한 알고리즘 마켓 메이킹에 훌륭한 선택입니다. 왜냐하면 이러한 종류의 트레이딩 작업에 집중되어 있기 때문입니다.
하지만 어떤 로봇을 사용하든, 항상 기억하는 것이 중요합니다:
🐦 트레이딩 작업의 수익성을 정의하는 것은 전략입니다. 알고리즘은 단지 전략을 컴퓨터 명령어로 번역하고 자동화된 방식으로 실행하는 것일 뿐입니다.
이익과 위험에 대한 간략한 메모
마켓 메이킹은 위험이 없고 항상 수익성 있는 트레이딩 작업이 아닙니다.다른 모든 거래 활동과 마찬가지로, 시장의 비효율성을 이용하기 위해 로봇을 실행하는 것은 그 자체의 위험/보상 특성을 가지고 있습니다.
따라서 실제 자금을 사용하기 전에, 이러한 유형의 트레이딩 메커니즘이 무엇인지, 그리고 어떤 종류의 위험에 노출될 것인지를 확실히 이해해야 합니다.
🐦 Hummingbot에서는
paper_trading명령어를 사용하여 모의 투자 모드(paper trading mode)를 활성화할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 자본을 위험에 빠뜨릴 필요 없이 실시간 시뮬레이션 환경에서 전략을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
저희 커뮤니티에 참여하세요
이것은 Hummingbot 아카데미의 첫 번째 글일 뿐이며, 앞으로 마켓 메이킹 및 차익거래와 관련된 다른 주제들, 일부 전략 분석을 포함하여 더 많은 글이 올라올 예정입니다. 우리의 목표는 여러분이 더 나은 마켓 메이커/차익거래자가 되는 방법을 배우도록 돕는 것입니다.
더 배우고 싶다면, 매주 새로운 글이 올라오는 저희 블로그 업데이트를 꼭 팔로우하세요.
다음 글을 기다리는 동안, 저희 디스코드 서버에 참여하는 것을 잊지 마세요. 이곳은 우리 커뮤니티가 마켓 메이킹과 차익거래, 그리고 Hummingbot을 사용하여 트레이딩 전략을 개선할 수 있는 모든 가능한 방법에 대해 이야기하는 곳입니다.
또한, Hummingbot 아카데미에서 다루었으면 하는 특정 주제가 있다면, 디스코드에서 저희 팀에 연락하거나 academy@hummingbot.io로 이메일을 보내주세요.
곧 뵙겠습니다. 모두 수익성 있는 트레이딩 세션이 되시기를 바랍니다!
Show original (English)
 # Welcome to Hummingbot Academy! If you reached this page, there is a high probability that you have been asking one of these questions: - What is a market maker? - What do market makers do? - How can I become a market maker? - How do I create a market making robot? - Then you are on the right place! Here at [Hummingbot](), our goal is to help you learn more about market making and how to use our free open-source robot to implement your own strategy. ## But what is a Market Maker? > A market maker (MM) is a firm or individual who actively quotes two-sided markets in a security, providing bids and offers (known as asks) along with the market size of each. ([source](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/marketmaker.asp)) If the above quote didn't made any sense to you, imagine a pawnshop:  Let's say that Susan has an old guitar, doesn't have much time to play anymore, and could use some cash; meanwhile in another part of town, Mike has been learning to play his friend's guitar and now thinks that he is good enough to invest some cash to buy his own, but a brand new one might be too expensive. Although we have two people that could close a deal, it might be difficult for them to find each other, or even to agree on a reasonable price for that guitar. This is where the pawn shop enter the picture: Instead of looking around for someone that wants to buy a guitar, Susan could sell her guitar to the pawnshop, and Mike could go there knowing that he would find one. The pawnshop owner is providing a service to both Susan and Mike. He offers an easy way to sell/buy what they want (providing liquidity) and a fair price, based on the demand for used guitar in the town (spread reduction). The pawnshop will be paid for this service by the difference in price he paid to Susan and the price he received from Mike (spread size). > 💡 A market maker, like a pawnshop owner, provides the same kind of service in financial markets. He provides liquidity and helps to reduce bid-ask spread sizes, taking his profits from the difference between his buy and sell orders (spread). ## How does market making happen in financial markets?¶ A financial market isn't much different from the real economy open markets. Every day, millions of people access some kind of trading platform, looking to close deals among a wide range of assets, including company shares, bonds, oil, gold, contracts, and cryptocurrencies. But instead of thousands of people gathering in the same place, holding signs and/or screaming for how much they are buying or selling something, financial assets markets use an order book, where all buy and sell offers are aggregated in the same place:  The order book is nothing more than a list of all buy and sell offers (with quantities and prices) available across all market participants. In the picture above, we can see the BTC/USD pair order book. If someone is looking to buy Bitcoin right now, he/she will have to pay $12,022.230 (the lowest ask price) and there is 0.578 BTC available at that price. But if someone wants to sell Bitcoin immediately, he/she will have to accept the price of $12,016.32 (the best bid price) for up to 0.016 BTC. > 💡 The difference between the lowest of offer prices and the highest of demand prices for a good or asset is called spread. Technically, any person that posts a buy or sell offer on the order book is acting as a market maker, while those who are accepting the prices offered on the order book is called a market taker. Acting as a market maker is conceptually similar to participating in the market as the "pawnshop owner", creating offers to buy an asset at a low price, and selling it at a higher price as fast as possible and as many times as possible. > 💡 While the most common trading/investing strategy looks to profit from big price changes, a professional market maker is trying to capitalize on smaller but more consistent price swings between two price levels. Most traders and investors want to see the market moving like this:  While market makers love to see market prices moving like this:  The price of an asset doesn't change at a constant flow but as waves, and while traders and investors are trying to find out if the sea is moving towards high or low tide, the market maker is watching the smaller waves on the beach. ## Bid-ask spread vs market maker spread Looking at the state of the order book on the picture we saw earlier, a market maker could post two offers: - Buy 1 Bitcoin for $12,016.320 (Bid price) - Sell 1 Bitcoin for $12,022.230 (Ask Price) When other market participants accept these prices, and a deal happens on both orders, the market maker will have a profit of $5.91 on this transaction. This is also known as the market Bid-Ask spread, and in this example above, it's the $5.91 profit the market maker received for completing both sides of the operation: $$ \frac{(12,022.23-12,016.32)}{12,016.32} = 0.049\% $$ Some exchanges even offer a way to visualize the ask-bid spread in real-time (along with the book depth, which is the accumulated size of all orders posted on the order book):  But this doesn't mean that a market maker must use always use this exact bid and ask prices. A market maker must still consider other factors when deciding what is going to be his operational spread, including: - Market bid-ask spread; - Transaction costs (including exchange fees and/or transfer fees); - Trade volume; - Market volatility; - Operational costs (electric bills, cloud server costs, etc.); - Any other costs related to the trading operation. There is no right or wrong answer to how big or small the market maker spread should be, and in the end, the spread is just a part of the market maker strategy. > 🐦 You can change your spread percentage on Hummingbot with the commands `config ask_spread` for sell orders and `config bid_spread` for buy orders. ## What goes into a strategy? Being a profitable market maker isn't only about choosing a spread size, starting to send limit orders to the order book, and then turning around and forgetting about it. Before starting a market making operation, you must ask yourself some questions: - Should I keep the spread fixed all the time? Should I change it depending on market conditions? - What should the size of my orders be? - What should I do when there is a price trend in the market, or if there is no clear trend? - How am I going to detect the market direction? - How long should my orders stay on the book? - If one side of the operation is filled, should I keep the opposing order until it is filled? - Do I want to accumulate more of one asset over time, or do I want to always have a 50/50 balance? - What should I do if there is price spike? - Should I care about the average buying cost? - When should I stay out of the market and for what reason, or should I trade all the time? - What can I lose, and how much am I putting at risk? - The answers to these questions determine your actions (and reactions) based on the market conditions and will ultimately define your strategy. A good market making strategy is nothing more than planning ahead on how you will react to market changes. But before you get scared with all of these questions and give up on market making, here is a tip: > 💡 Start Small. Don't try to have all the answers to your strategy beforehand, but focus on one parameter at a time, testing and watching what happens in different market situations. Over time, add another parameter and do more testing and watch how all the pieces are working together. You are not going to find a cookie cutter, ready-to-use, one-size-fits-all and always profitable strategy/parameters just simply lying around, but after some time, you will start to understand the good and the bad of each strategy, and after experimenting with some of them will find one that fits your goals. > 🐦 On Hummingbot, you can combine different settings in different ways using the `config` command to build a wide variety of strategies. Check out the pure market making reference guide to see what each parameter is used for. ## Automated trading and market making So, trading robots... That is probably another reason why you are reading this article; you are not just looking to become a market maker, you are looking to setup a market making robot to do all of the hard work. After all, Hummingbot is an open-source trading robot, available for free to anyone who wants to start an automated trading strategy. While it is possible to do market making operations manually, a trading robot allows your strategy to be executed in a precise way, remove the emotional factor (greed and fear), and even create safety measures for better risk control. But not all robots are made equal, and depending on what kind of strategy you are going to use (high-frequency, low-frequency, trend following, grid, straddle, quant... there are a lot of possibilities), one bot might do a better job than others. After all, a trading robot is a tool and we must use the right tool for the job. Hummingbot is a great choice for algorithmic market making for the cryptocurrency markets because it is focused on this kind of trading operation. But no matter what robot you choose to use, it's always important to remember: > 🐦 What defines the profitability of a trading operation is the strategy. The algorithm is only the strategy translated into computer instructions and executed in an automated way. ## A quick note on profit and risk Market making is not a risk-free, always profitable trading operation. Like any other trade activity, running a robot to capitalize on market imperfections comes with its own set of risk/reward features. Therefore, before you start using real funds, make sure that you understand what the mechanics of this type of trading are and what kind of risks you will be exposing yourself to. > 🐦 With Hummingbot you can enable the paper trading mode using the command paper_trading, which allows you to test your strategy in a real-time simulated environment, without the need to put your capital at risk. ## Join our community This is only the first article of the Hummingbot Academy and there are a lot more articles to come where we will talk about other topics related to market making and arbitrage trading, including some strategy analysis. Our objective is to help you learn how to become a better market maker/arbitrageur. If you want to learn more, make sure to follow our blog updates for new articles every week. While you wait for the next post, remember to join our Discord server, a place where our community talks about market making and arbitrage, and all the possible ways you can use Hummingbot to improve your trading strategies. Also, if there is any specific topic you want us to cover on the Hummingbot Academy, contact our team on Discord, or send an email to academy@hummingbot.io. See you soon, and I wish you all a profitable trading session!위 블로그 글이 와닿지 않을 수 있습니다. 그래서 Pure Market Making(PMM)에 대한 조금 더 구체적인 예시를 현재 업비트 호가창으로 보여보겠습니다.
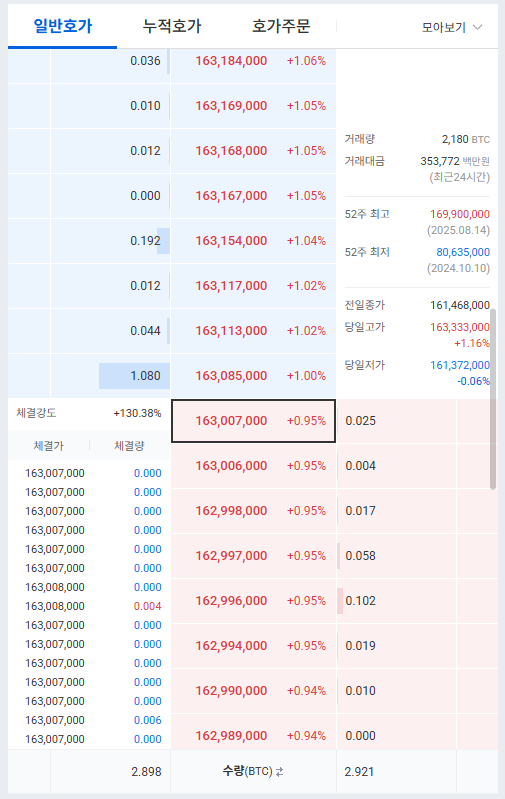
현재 BTCKRW의 호가창 상황은 아래와 같습니다.
- 매수 최우선호가: 163,007,000원
- 매도 최우선호가: 163,085,000원
- 스프레드: 78,000원 (약 0.048%)
- 중간가격(mid-price): (163,007,000 + 163,085,000) ÷ 2 ≈ 163,046,000원
이제 여기에 가정을 해보겠습니다. 매수/매도 스프레드 0.1%와 주문 리프레시 시간 10초 그리고 주문 크기 0.01 BTC 라고 가정해보겠습니다. 이제 각 시간마다 상황을 정리해보면,
- t=0: 전략은 중간가격 163,046,000원을 기준으로 계산
- 매수 주문: 163,046,000 × (1 - 0.001) ≈ 162,883,000원
- 매도 주문: 163,046,000 × (1 + 0.001) ≈ 163,209,000원
- 따라서 주문장은:
- 매수 주문 0.01 BTC @ 162,883,000원
- 매도 주문 0.01 BTC @ 163,209,000원
- 즉, 기존 최상단 호가보다 약간 아래/위에 나만의 주문을 배치
- t=5: 시장에서 누군가 매도 주문을 내서 내 매수 주문(162,883,000원)이 체결됨.
- 나는 0.01 BTC를 보유하게 됨. 전략은 다음 틱에서 새로운 매수 주문을 다시 배치하여 균형 유지.
- t=10: 전략은 기존 주문을 취소하고 새로 계산
- 만약 가격이 변동해 중간가격이 163,200,000원으로 올랐다면
- 매수 주문: 163,037,000원
- 매도 주문: 163,363,000원
- 주문이 시장 변화에 맞춰 다시 깔림
- 만약 가격이 변동해 중간가격이 163,200,000원으로 올랐다면
수익은 다음과 같이 정리됩니다.
- 내가 162,883,000원에 매수한 0.01 BTC를, 이후 누군가가 163,209,000원에 매수(즉 내 매도 주문 체결)하면
- 차익 = (163,209,000 - 162,883,000) × 0.01 = 3,260원
- 이 작은 차익을 초당 수십·수백 번 반복하면서 수익 확보
정리하면, 지금 매수·매도 호가 차이가 좁은 시장에서도, 마켓메이킹은 중간 가격(mid-price) 기준으로 스프레드를 잡고 반복적으로 주문 갱신을 해서 안정적으로 수익을 쌓는 구조입니다. 그리고 중간 가격을 어떤 기준으로 두느냐에 따라서 성능이 많이 좌우됩니다.
이러한 PMM의 가장 리스크 중 하나는 바로 한 방향(상승장/하락장)으로 쭉 밀어붙이는 장세일 경우입니다. → 재고 리스크(Inventory Risk)는 다음 포스팅에서 조금 더 이야기 해보도록 하겠습니다.
- 하락장 (계속 가격이 떨어질 때)
- 전략은 계속 저가 매수 주문이 체결됨 → BTC 재고(Inventory)가 늘어남.
- 하지만 시장 가격이 계속 내려서, 내가 내놓은 매도 주문(조금 높은 가격) 은 체결되지 않음.
- 결과적으로 BTC 재고만 쌓이고 평가손실(미실현 손실) 발생.
- 예시: 1BTC를 163,000,000원 근처에서 여러 번 나눠 샀는데, 가격이 160,000,000원까지 내려가면 → 평가손실 -3,000,000원. 전략은 틱마다 새로운 매도 주문을 내겠지만, 시장이 안 올라오면 체결이 안 됨.
- 상승장 (계속 가격이 오를 때)
- 전략은 계속 고가 매도 주문이 체결됨 → KRW(현금)는 늘어나지만 BTC 재고가 줄어듦.
- 그런데 가격이 계속 올라가면, 내가 판 가격보다 훨씬 더 높은 가격에서 BTC를 다시 사야 할 수 있음.
- 결과적으로 기회비용 손실 발생 (BTC를 싸게 판 뒤, 비싸게 다시 사야 하는 상황).
- 예시: 0.1BTC를 163,200,000원에 팔았는데, 가격이 165,000,000원까지 올라감. 다시 매수 주문을 갱신하려면 164,800,000원 같은 높은 가격에 매수 주문을 걸어야 해서 불리함.
이러한 추세장에서 극복하는 방법은 아래와 같이 크게 3가지입니다.
- 인벤토리 스큐(Inventory Skew)
- 내가 BTC를 너무 많이 들고 있으면 → 매도 주문 위주로 내고, 매수 주문은 줄임.
- 반대로 현금만 남아 있으면 → 매수 주문 위주로 내서 밸런스를 맞춤.
- 스프레드 동적 조정(Dynamic Spread)
- 추세가 강하면 스프레드를 넓혀서 리스크를 줄임.
- 예: 평소 ±0.1% → 변동성 클 때 ±0.5%
- 헤지(Hedging)
- 선물(Futures)이나 다른 거래소를 활용해서 반대 포지션을 잡음.
- 예: 업비트에서 현물 마켓메이킹을 하면서, 바이낸스에서 반대 방향 선물 포지션을 잡아 가격 리스크를 줄임.
참고자료
- https://github.com/hummingbot/hummingbot
- https://hummingbot.org/blog/what-is-market-making
- Market Making under a Weakly Consistent Limit Order Book Model
