What is Inventory Risk?

안녕하세요, Hummingbot 커뮤니티 여러분!
오늘부터 저는 모든 종류의 트레이딩 작업에 포함되는 가장 중요한 요소라고 생각하는 것, 바로 리스크와 리스크 관리에 대해 이야기 시작하겠습니다.
우리 시대의 가장 위대한 투자자 중 한 명이 말했듯이:
“리스크는 당신이 무엇을 하고 있는지 모르는 데서 온다.” ~ 워런 버핏

모든 종류의 금융 활동에는 다양한 수준의 리스크가 있으며, 마켓 메이킹도 예외는 아닙니다.
미래의 이익을 상상하고 예측하며 차세대 워런 버핏이 되는 것을 공상하는 것이 더 흥미로워 보일 수 있지만, 투자의 현실적이고 덜 화려한 부분, 그리고 아마도 가장 중요한 부분은 무엇이 잘못될 수 있는지 파악하고 그로 인해 발생할 수 있는 손실을 완화하는 방법을 찾는 것입니다.
리스크와 리스크 관리에 대해 다룰 내용이 많지만, 오늘은 마켓 메이킹과 관련된 주요 리스크 중 하나인 재고 위험(inventory risk)에 초점을 맞추겠습니다.
오늘 글에서 다룰 내용은 다음과 같습니다:
- 재고 가치란 무엇인가?
- 재고 위험이란 무엇인가?
- Hummingbot으로 재고 위험을 완화하는 방법
그리고 언제나처럼, 저희 디스코드의 #trader-chat에 참여하여 커뮤니티와 함께 마켓 메이킹 전략을 개선하는 방법에 대해 논의하는 것을 환영합니다.
1️⃣ 재고 위험이란 무엇인가?
마켓 메이커로서, 당신의 주요 역할은 다른 시장 참여자들에게 유동성을 제공하는 것입니다.
당신은 다른 트레이더들에게 서비스를 제공하며, 다른 모든 사람들에게 자산을 사고팔겠다고 제안하고, 그 대가로 매수 호가와 매도 호가 사이의 스프레드 크기(낮게 사서 높게 파는 주문)를 통해 보상을 받습니다.
이 서비스를 제공하기 위해, 마켓 메이커는 주문을 생성하고 거래를 하기 위해 일정량의 자산을 재고로 보유해야 하며, 이 재고에는 그에 상응하는 가치가 있습니다.
재고 가치 (Inventory Value)
모든 시장 참여자가 이미 알고 있듯이, 자산의 가격은 끊임없이 변하며, 모든 트레이더는 자신이 이익을 내고 있는지 아닌지를 추적할 방법이 있어야 합니다.
성과를 추적하는 한 가지 간단한 방법은 트레이더가 소유한 자산의 총 가치를 비교하는 것입니다.
예를 들어, 현재 당신이 0.46820424 BTC와 14.6426 ETH를 소유하고 있다고 가정해 봅시다:
1일차 재고
첫째 날, 당신의 자산의 현재 가치는 10,000달러입니다. 실제로 USD를 전혀 소유하고 있지 않고 BTC와 ETH만 소유하고 있더라도, 현재 시장 가격으로 BTC와 ETH를 10,000달러로 전환할 수 있는 능력이 있습니다.
재고 가치는 벤치마크 자산 대비 자산의 가치가 변할 수 있기 때문에 시장 가격의 변화에 따라 변동될 수 있습니다.
만약 당신이 거래하지 않았다면, 2일차에도 시작 포트폴리오와 동일한 양의 BTC와 ETH를 가지고 있을 것입니다.
2일차 재고
그러나 이 자산들의 USD 가격이 변했기 때문에, 재고 가치는 9,761.38달러로 하락했습니다. BTC 가치는 올랐지만, ETH 가치는 떨어졌습니다.
재고 가치는 포트폴리오에 보유된 모든 자산의 현재 가치로, 선택한 벤치마크 또는 기준 자산(예: USD)으로 정량화됩니다.
가치를 결정하기 위한 벤치마크 기준 자산 선택은 투자자마다 다릅니다. 예를 들어, 미국 투자자는 USD를 사용할 수 있지만, 유럽 투자자는 유로를 선택할 수 있습니다. 이는 적어도 현재로서는 그들의 비용(음식, 임대료) 대부분이 여전히 USD(또는 유로)로 표시되고, 법정화폐가 여전히 그들의 자산과 구매력의 벤치마크이기 때문입니다.
2️⃣ 트레이딩에서의 재고 위험
마켓 메이커의 주요 목표는 시간이 지남에 따라 총 재고 가치를 높이는 것입니다. 더 일반적이고 보편적인 투자 접근 방식은 미래에 가치가 상승할 자산을 사려고 노력하는 것입니다. 이것은 “방향성” 투자로, “저렴한” 자산을 사서 자산 가격이 결국 오를 것이라고 베팅하는 것입니다.
반면에, 마켓 메이커는 시간이 지남에 따라 점진적인 매수-매도 스프레드를 포착하고 축적함으로써 포트폴리오 가치를 높이려고 합니다. 마켓 메이커는 지속적으로 자산을 동시에 사고팔겠다고 제안하며, 팔려는 가격보다 약간 낮은 가격에 사겠다고 제안합니다. 마켓 메이커가 매수와 매도를 완료할 수 있다면, 그는 이 차이인 “매수-매도 스프레드”의 일부를 포착할 수 있습니다. 마켓 메이커가 이 매수-매도 사이클을 더 많이 완료할수록, 더 많은 이익을 축적할 수 있습니다.
첫 번째 아카데미 글에서 언급했듯이, 마켓 메이커에게 이상적인 상황은 가격이 추세 없이 움직일 때입니다:
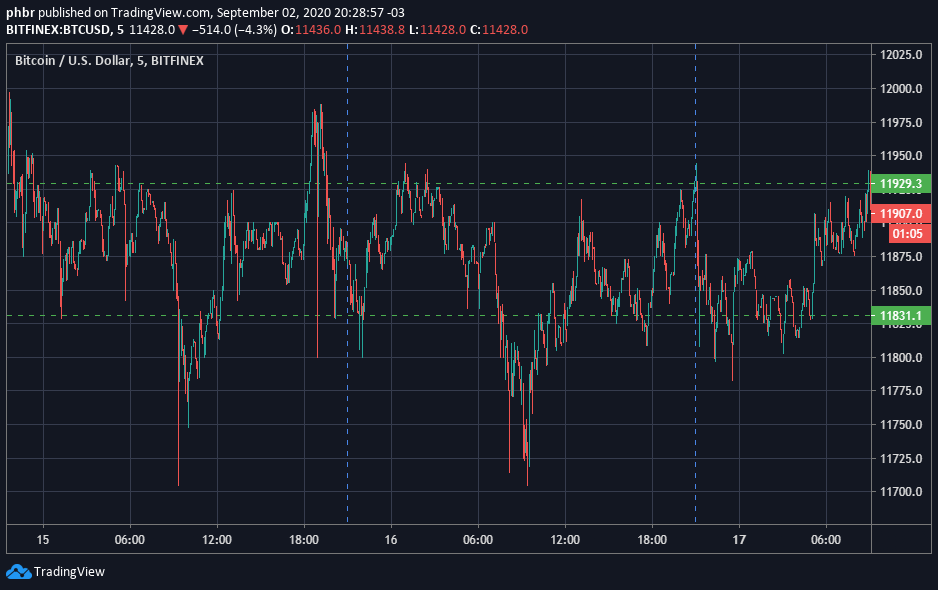
가격이 일정 범위 내에서 거래될 때, 마켓 메이커의 매수와 매도가 동일한 빈도로 체결될 가능성이 높아지고, 마켓 메이커가 점진적인 이익을 축적할 가능성이 높아집니다.
문제는 가격이 한 방향으로 추세를 보이기 시작할 때 시작됩니다.예를 들어, 가격이 하락 추세를 보이기 시작하면, 그의 매수 주문은 체결되기 시작하지만, 매도 주문은 체결되지 않습니다:
출처: 저희 커뮤니티 멤버 @Christian Feldmann
이 상황의 결과는 마켓 메이커가 가치를 잃고 있는 자산의 재고를 늘리기 시작하여, 시간이 지남에 따라 총 재고 가치가 감소하게 된다는 것입니다.
결국 가격이 수익성 있는 수준으로 돌아와 마켓 메이커가 자신의 재고를 수익성 있는 가격에 팔 수 있을 수도 있습니다. 하지만 문제는, 이 상황이 지속되고 가격이 계속 하락하면, 모든 마켓 메이커의 재고가 한쪽에 묶이게 된다는 것입니다.
어떤 시점에서, 마켓 메이커는 자신의 운영을 중단하고 더 나은 가격을 기다릴지, 아니면 운영을 계속하기 위해 손실을 보고 재고를 팔기 시작할지 결정해야 합니다.
이것은 소매점 관리자가 더 나은 가격에 공급업체로부터 더 많은 제품을 사서 재고를 늘리기 시작했지만, 그의 고객들은 그의 제품을 사는 데 별로 관심이 없는 것과 유사합니다.
마켓 메이커가 매수와 매도 주문을 모두 생성하더라도, 양쪽이 모두 체결될 것이라는 보장은 없습니다. 위 예시에서, 매수 주문은 계속 체결되지만 매도 주문은 결코 체결되지 않습니다. 이것은 또한 마켓 메이커를 보유 재고량의 변동 위험에 노출시킵니다. 예를 들어, 마켓 메이커는 가치를 잃고 있는 자산을 축적할 수 있습니다. 반대로, 가치가 상승하고 있는 자산을 팔아버릴 수도 있습니다.
재고 위험은 마켓 메이커가 자신의 재고에 대한 구매자를 찾지 못할 확률로, 정확히 잘못된 시점에 자산을 더 많이 보유하게 될 위험을 초래합니다. 예를 들어, 가격이 하락할 때 자산을 축적하거나 가격이 상승할 때 너무 일찍 파는 것입니다.
3️⃣ Hummingbot을 이용한 재고 위험 관리
재고 위험은 마켓 메이킹의 주요 위험입니다. 이것이 Hummingbot이 재고 위험을 완화하기 위해 설계된 많은 전략 사용자 정의를 허용하는 이유이며, 우리 팀이 이와 관련된 더 많은 기능을 계속 개발하는 이유입니다.
이러한 유연성을 통해 마켓 메이커는 다양한 방법으로 운영 위험을 완화하고, 자신의 주요 전략에 맞는 조정을 할 수 있습니다.
재고 위험을 통제할 수 있는 몇 가지 예는 다음과 같습니다:
history 명령어
history 명령어는 과거 거래 내역과 봇 시작 이후 총 자산량의 변화 요약을 표시합니다.
각 측면의 재고가 얼마나 변했는지 시각화하고 총 가치와 비교하는 좋은 방법입니다.
인벤토리 스큐 (Inventory skew)
config inventory_skew_enabled를 사용하면 봇이 매 새로운 주문마다 order_amount(주문 수량)를 변경하여 총 재고 크기를 재조정합니다.
재고에 있는 각 자산의 목표 비율은 config inventory_target_base_pct 명령어를 통해 정의할 수 있으며, 재고가 이 비율에서 얼마나 벗어날 수 있는지는 config inventory_range_multiplier를 사용하여 정의할 수 있습니다.
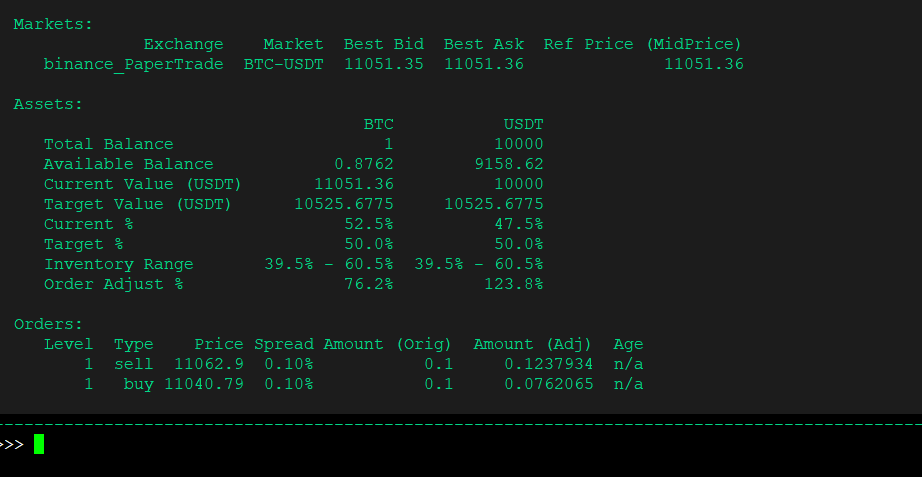
위에서 볼 수 있듯이, 재고에 USDT보다 BTC가 더 많으며, 봇은 사는 것보다 더 많이 팔고 있습니다.
이 매개변수는 재고 보호용으로 사용될 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 마켓 메이커가 한 방향으로 추세가 형성되는 것을 발견하면: BTC 가격이 상승 추세라면, 마켓 메이커는 config inventory_target_base_pct를 70으로 설정하여 더 많은 BTC를 축적하기 시작할 수 있습니다.
또한, USD가 아닌 페어(예: ETH-BTC)를 거래하는 경우 특히 유용합니다. 트레이더는 각 자산의 가치를 USD와 비교하여 평가하고, 미래에 자산 중 하나의 가치가 더 높아질 것이라고 생각하면 인벤토리 스큐를 조정할 수 있습니다.
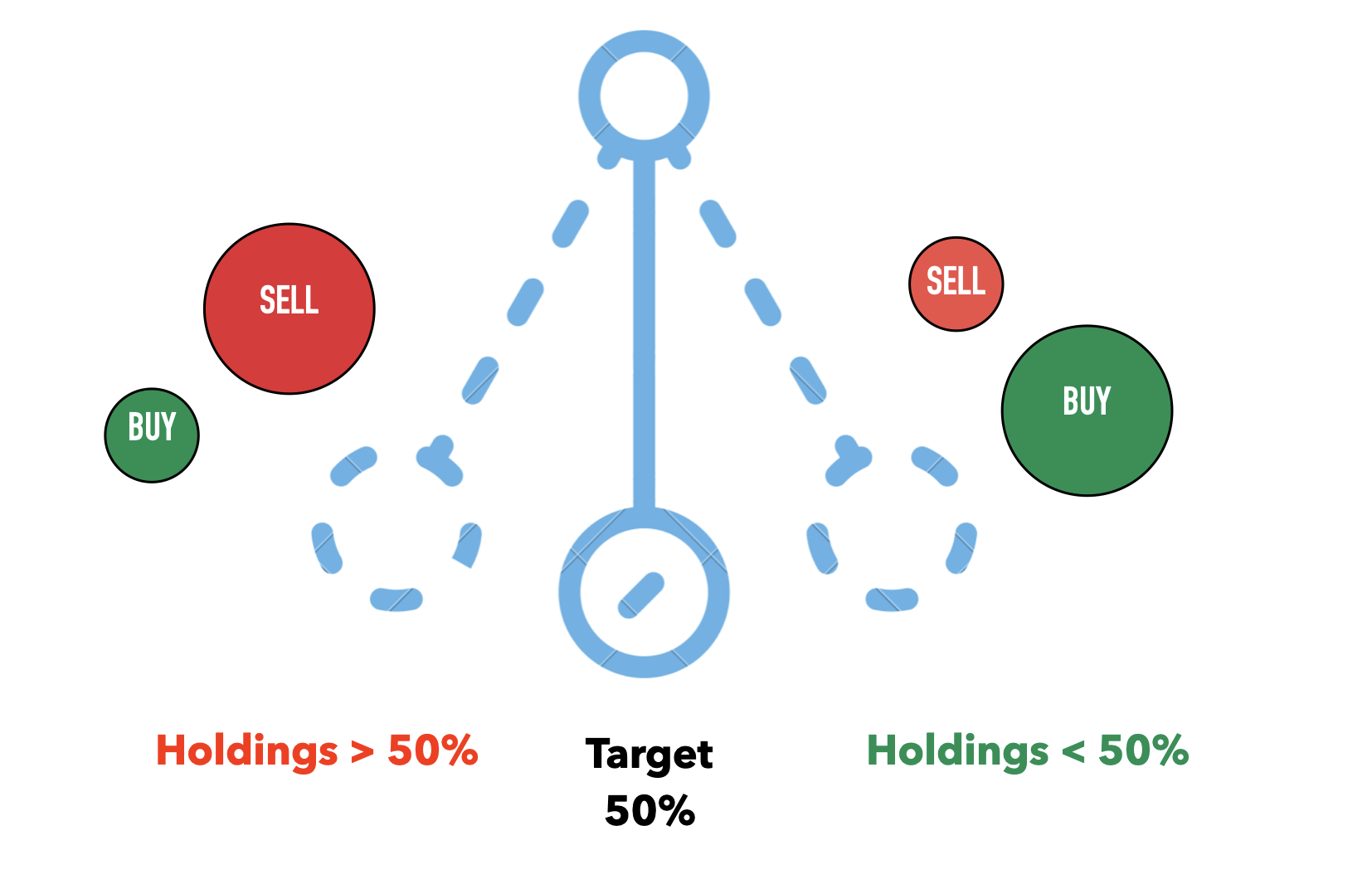
인벤토리 스큐는 끊임없는 시계추 균형잡기와 같습니다. 트레이더가 한 자산을 더 많이 축적하면, Hummingbot은 목표 보유량으로 돌아가기 위해 주문 크기를 조정(매수 축소, 매도 확대)하며, 그 반대의 경우도 마찬가지입니다.
인벤토리 스큐는 재고량이 너무 많이 변동하는 위험을 최소화하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 50%와 같은 목표 비율을 유지하려고 노력하면 마켓 메이커가 계속해서 매수 및 매도 양쪽 호가를 제시하고 매수-매도 스프레드를 포착할 수 있도록 보장하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
체결 주문 지연 (Filled Order Delay)
filled_order_delay 매개변수를 통해, 마켓 메이커는 이전 주문이 체결된 후 봇이 후속 새 주문을 생성하는 데 지연 시간을 설정할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, filled_order_delay = 300으로 설정하면 봇이 생성한 주문이 체결될 때, 다음 주문 쌍은 300초 후에만 생성됩니다.
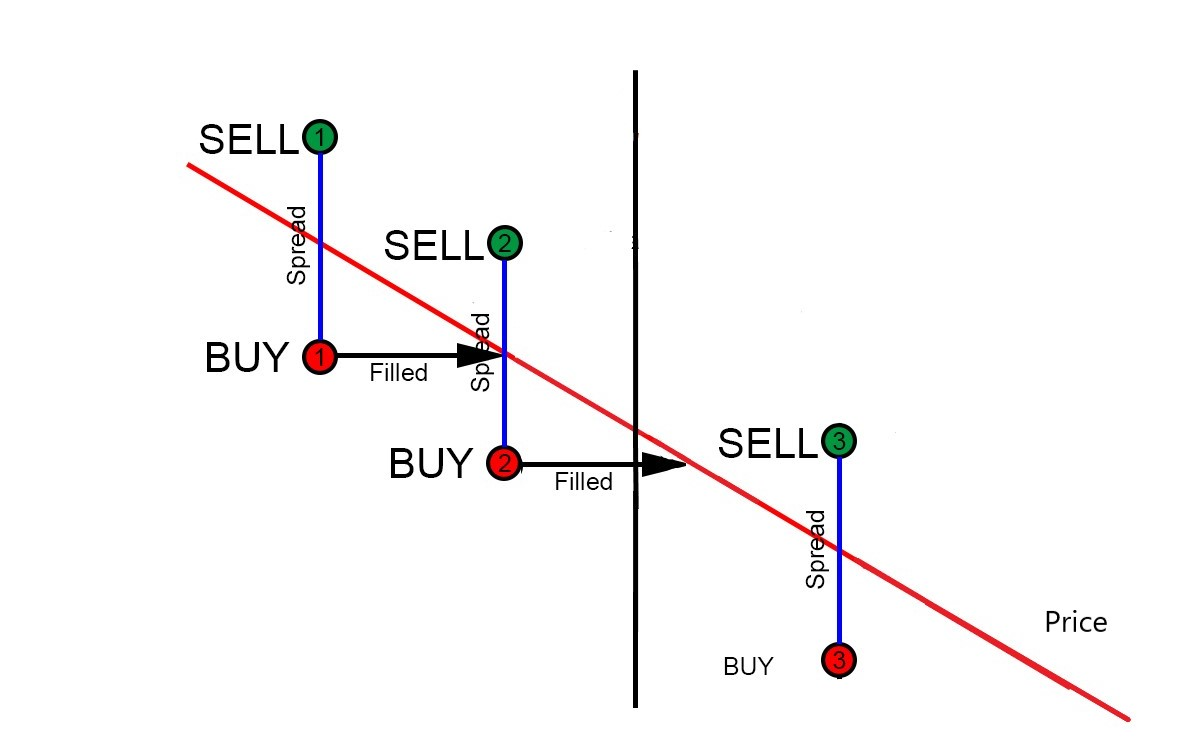
이것은 가격이 추세일 때 기간을 관리하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 예를 들어, 아래 다이어그램에서 가격이 하락 추세일 때, 주문이 새로고침될 때마다 매수 주문이 계속 체결됩니다.
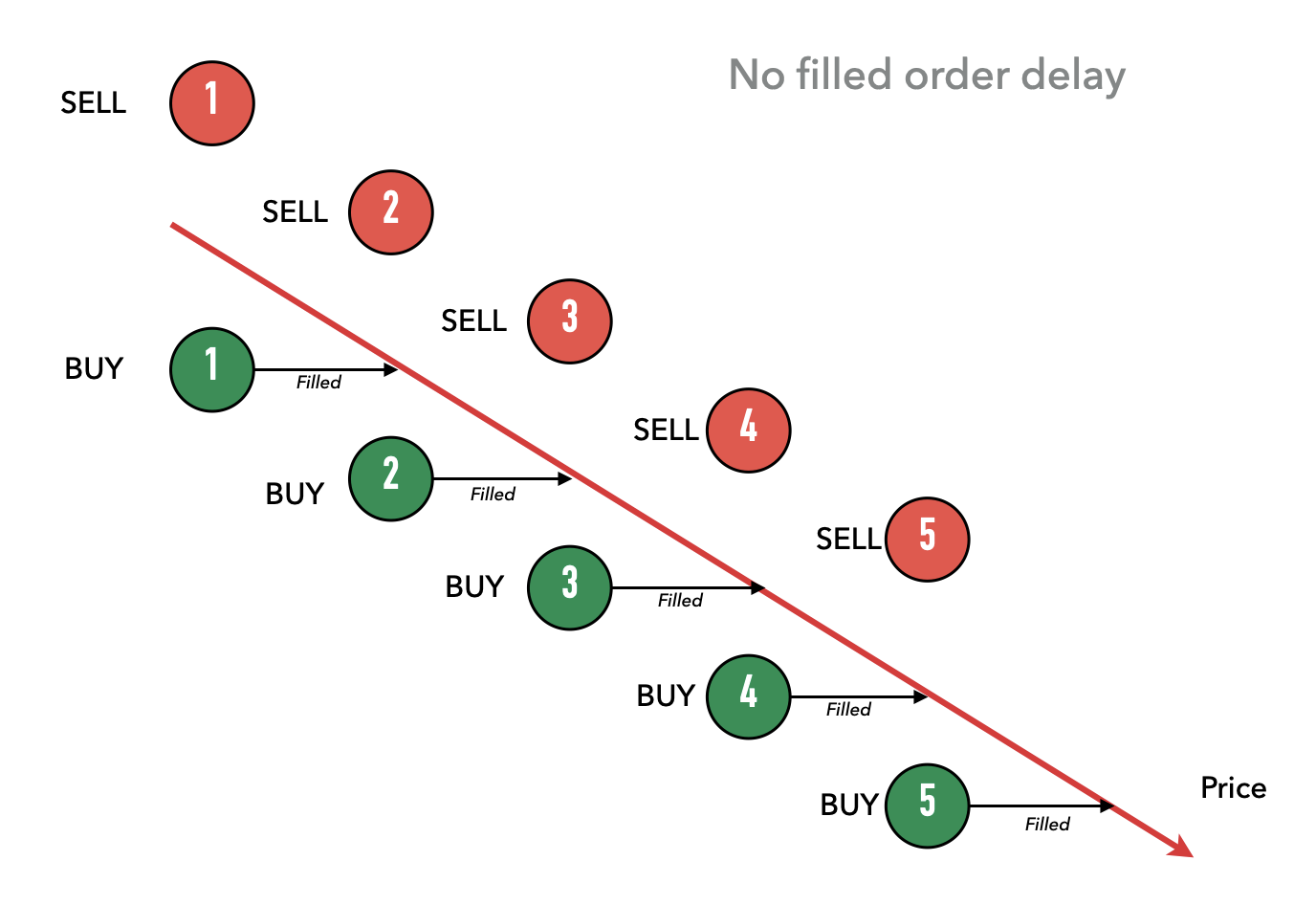
이것이 반복되고 계속되면, 마켓 메이커는 단 몇 번의 주문 새로고침 주기 만에 빠르게 많은 양의 자산을 축적하게 될 수 있습니다. 위 예시에서, 트레이더는 자산을 5번 샀습니다.
체결된 주문과 새 주문 배치 사이에 지연을 도입함으로써, 이는 주문 간의 간격을 두고 자산의 잠재적 축적을 억제하며, 가격 추세가 안정될 시간을 벌어줍니다.
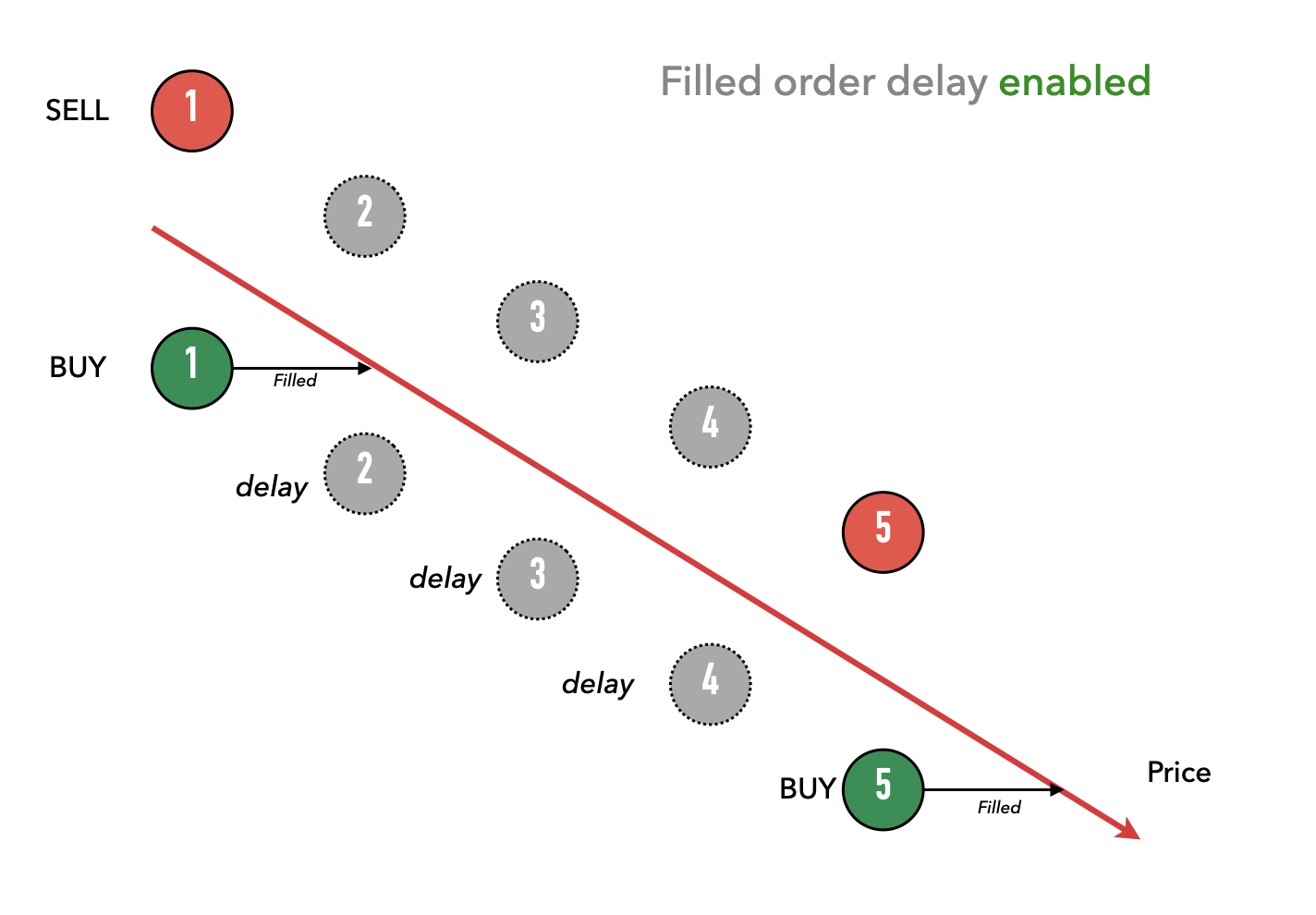
위에서 볼 수 있듯이, 1번 기간의 매수 주문이 체결되었기 때문에 봇은 2, 3, 4번 기간에 주문을 내지 않았습니다. 따라서 이 하락 가격 추세에서 봇은 두 번만(1번과 5번 기간) 샀지만, 체결 주문 지연이 활성화되지 않았을 때는 봇이 다섯 기간 모두에서 샀을 것입니다.
행잉 오더 (Hanging Orders)
행잉 오더는 Hummingbot에게 동시에 생성된 매수와 해당 매도 주문을 한 쌍으로 취급하도록 지시하는 기능입니다. 한쪽이 체결되면, 봇은 쌍의 다른 쪽을 미체결 상태로 유지하여, 그쪽이 결국 체결될 기회와 가능성을 만듭니다:
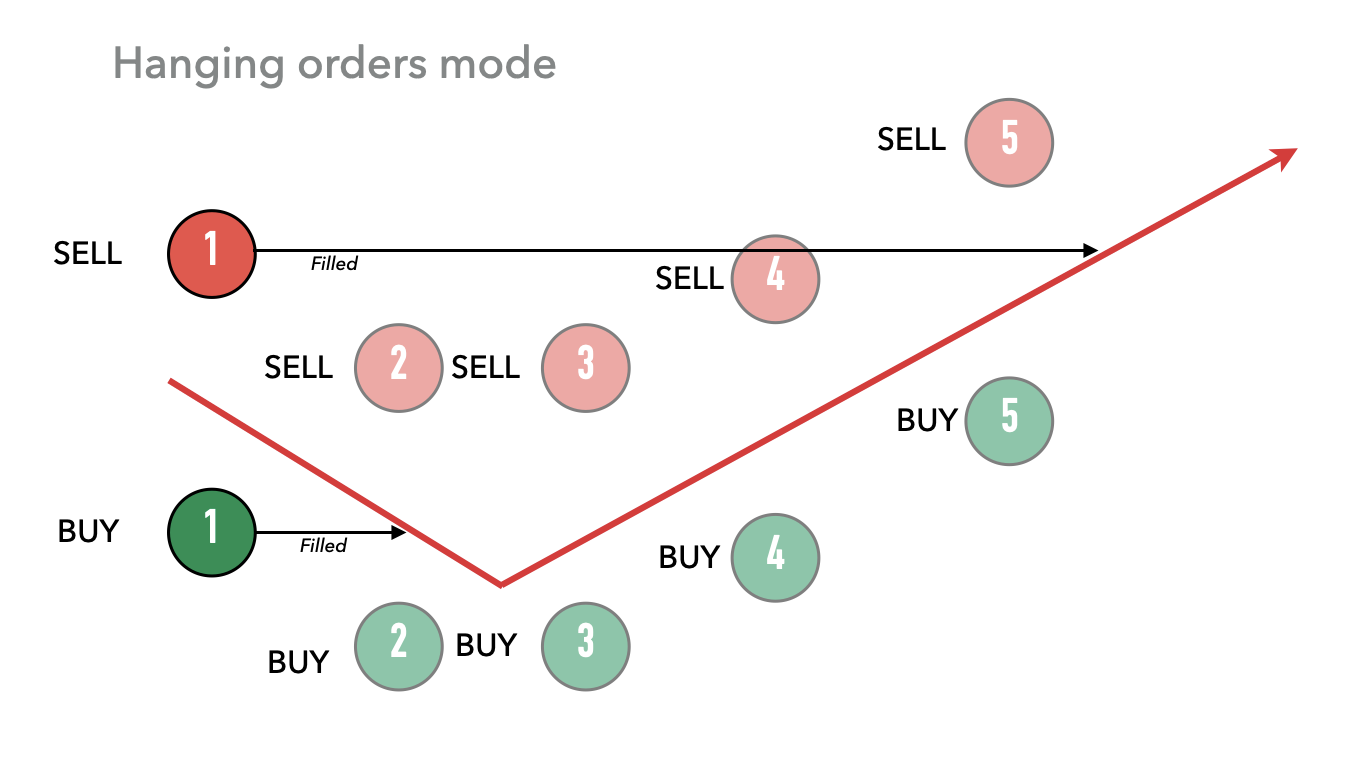
위 예시에서, 1번 기간의 매수 주문이 체결되었습니다. 하지만 행잉 오더 모드가 활성화되었기 때문에, 1번 기간의 원래 매도 주문은 새로고침 주기(2번 기간) 동안 취소되지 않고 미체결 상태로 남아 있습니다. 그동안 봇은 새 주문을 생성하는 작업을 계속합니다(2번부터 5번 기간 참조). 예시에서 가격 방향이 바뀌었고, 결국 어느 시점에서 행잉 매도 주문이 5번 기간 즈음에 체결되었습니다.
이 전략의 이점은 쌍이 “완료”되고 균형을 이룰 가능성을 만든다는 것입니다. 위 예시에서, 행잉 오더를 통해 트레이더는 결국 매수와 매도를 일치시키면서 매수-매도 스프레드를 확정할 수 있습니다.
핑퐁 (Ping Pong)
핑퐁 전략은 매수와 매도의 균형을 유지하려는 또 다른 전략입니다. 이는 체결된 주문의 반대쪽에만 주문을 생성함으로써 그렇게 합니다. 예를 들어:
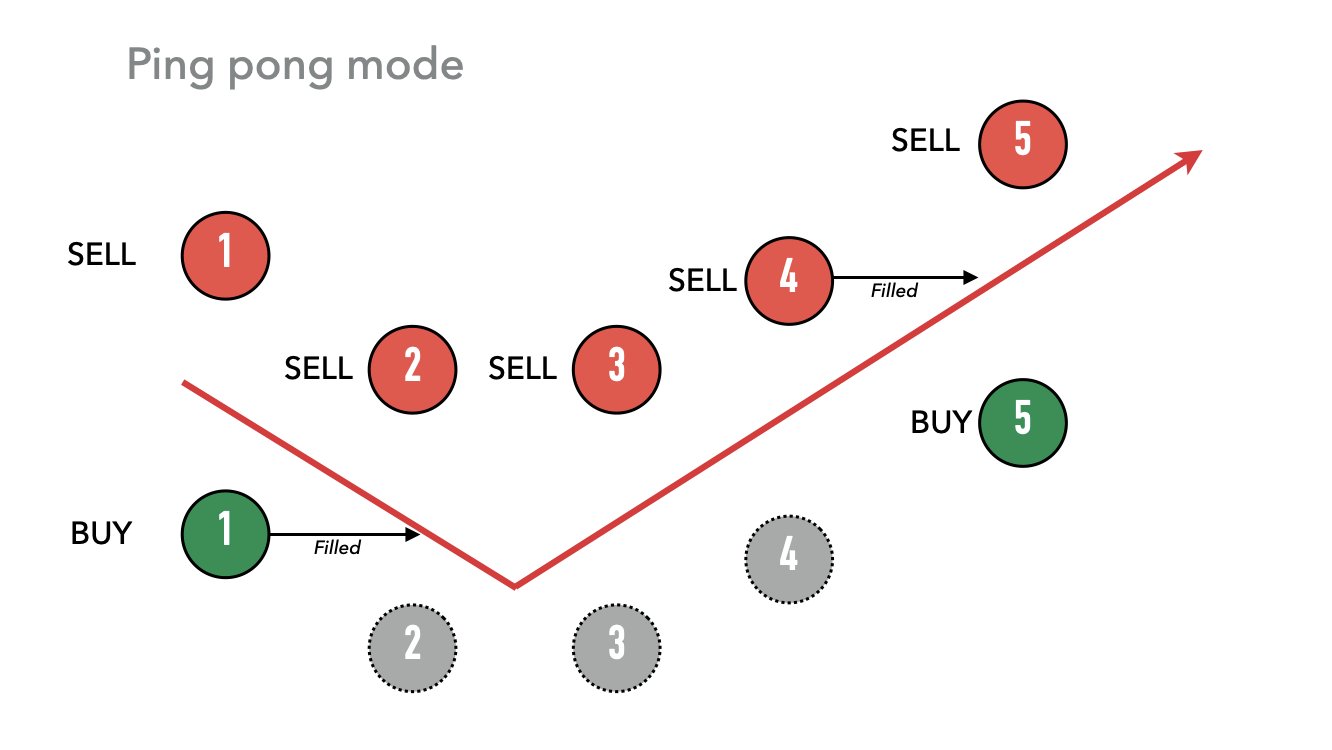
1번 기간의 매수 주문이 체결되었기 때문에, 봇은 매수 주문 배치를 중단하고 매도 주문만 배치합니다(2-4번 기간). 매도 주문이 결국 체결될 때(4번 기간)에만 봇은 매수 및 매도 주문 생성을 재개합니다(5번 기간).
가격 추세를 따르기 위해 한쪽 스프레드 조정
보통 마켓 메이커들은 동일한 bid_spread와 ask_spread를 적용합니다. 이것은 횡보장에서 훌륭합니다. 왜냐하면 가격이 범위 내에서 움직일 것이고, 자연스럽게 재고는 50/50 비율을 유지하는 경향이 있으며, 마켓 메이커는 스프레드에서 이익을 얻을 것이기 때문입니다.
하지만 위에서 말했듯이, 추세장에서는 문제가 됩니다. 재고가 덜 가치 있는 자산 쪽으로 축적되기 시작할 수 있기 때문입니다.
이를 완화하는 한 가지 옵션은 한쪽의 스프레드를 좁혀서 해당 주문이 먼저 체결될 확률을 높이는 것입니다.
예시:
마켓 메이커인 마크는 BTC-USDT에서 bid_spread = 0.5와 ask_spread = 0.5로 운영을 시작했습니다. 하지만 가격이 상승 추세를 보이기 시작하여, 그는 매개변수를 bid_spread = 0.1과 ask_spread = 0.9로 변경했습니다.
그렇게 하면, 그의 총 스프레드는 여전히 동일하지만(1%), 그의 매수 제안은 이제 매도 제안보다 체결될 확률이 더 높아집니다.
스크립트 (Scripts)
Hummingbot에는 내장된 스크립트 기능이 있어, 자신만의 맞춤 전략을 만들 수 있으며, 봇은 당신이 원하는 어떤 전략에든 기반하여 매개변수를 조정할 것입니다.
필요한 것은 파이썬으로 코딩하는 방법을 알고, Hummingbot 코드 베이스와 통합된 .py 파일을 만들고, config script_enabled 명령어를 통해 스크립트를 활성화하는 것뿐입니다(스크립트에 대한 더 많은 정보는 여기에서 찾을 수 있습니다).
이 레딧 유저가 물었던 것처럼, 자동화된 마켓 메이킹(AMM) 로직을 복제하는 스크립트를 만들 수도 있습니다.
저희 개발팀은 스크립트 모듈에 대한 많은 개선 작업을 하고 있습니다. 이것이 Hummingbot 사용자들이 자신들의 맞춤 전략을 구현할 수 있는 주요 방법이기 때문입니다.
4️⃣ 마무리하며
요즘 트레이더가 되는 것은 정말 쉽습니다.
하지만 좋은 트레이더가 되는 것은 또 다른 이야기입니다.
제가 금융 시장을 공부한 이 몇 년 동안 깨달은 것은, 좋은 트레이더와 나쁜 트레이더를 구분하는 주요한 것은 그들이 리스크에 대해 얼마나 알고 있고 그것을 어떻게 관리하는가 하는 것입니다.
좋은 전략은 돈을 버는 최선의 방법을 찾는 것뿐만 아니라, 시장이 당신의 계획과 반대로 움직일 때 무엇을 해야 할지 아는 것이기도 합니다.
각 유형의 트레이딩 작업과 관련된 위험을 이해하는 것은 지속 가능하고 수익성 있는 전략을 찾는 데 필수적입니다.
마켓 메이킹과 관련된 주요 위험은 재고 위험입니다. 어떤 시장에서든 마켓 메이커로 운영하려는 모든 사람에게 이것을 이해하고 완화하는 방법을 배우는 것이 우선순위가 되어야 합니다.
이 글은 이 주제에 대한 설명과 Hummingbot을 사용하여 이 위험을 관리하는 몇 가지 실용적인 방법을 다루었지만, 이것은 매우 중요한 주제여서 ‘Dealing with the Inventory Risk: A Solution to the Market Making Problem‘이나 ‘Market making with asymmetric information and inventory risk‘와 같은 방대한 양의 연구 논문이 있으며, 결국 가까운 미래에 이 주제에 대해 더 많이 이야기할 것입니다.
또한, 최근 자동화된 마켓 메이커 프로토콜(유니스왑과 같은 유동성 풀), 유동성 채굴, 그리고 탈중앙화 금융(DeFi)과 관련된 모든 것의 부상과 함께, 수동적인 마켓 메이커가 되려는 경우 위험을 이해하는 것이 정말 중요합니다.
그러니 저희 블로그를 계속 지켜봐 주세요. 곧 이들 프로토콜과 전통적인 오더북 마켓 메이킹의 주요 차이점을 비교하는 글을 게시할 예정입니다.
다음 주에 뵙겠습니다.
5️⃣ 저희 커뮤니티에 참여하세요
더 배우고 싶다면, 매주 새로운 글이 올라오는 저희 블로그 업데이트를 꼭 팔로우하세요.
다음 글을 기다리는 동안, 저희 디스코드 서버에 참여하는 것을 잊지 마세요. 이곳은 우리 커뮤니티가 마켓 메이킹과 차익거래, 그리고 Hummingbot을 사용하여 트레이딩 전략을 개선할 수 있는 모든 가능한 방법에 대해 이야기하는 곳입니다.
또한, Hummingbot 아카데미에서 다루었으면 하는 특정 주제가 있다면, 디스코드에서 저희 팀에 연락하거나 academy@hummingbot.io로 이메일을 보내주세요.
곧 뵙겠습니다. 모두 수익성 있는 트레이딩 세션이 되시기를 바랍니다!
다음 주에 뵙겠습니다!
Show original (English)
 Hello again Hummingbot community! Today we will start to talk about what I consider the most important factor that is part of all types of trading operations: risk and risk management. As one of the biggest investors of our time once said: "Risk comes from not knowing what you're doing." ~ Warren Buffett  All kinds of financial operations have varying degrees of risk, and market making is no different. While it seems more exciting to imagine and project future gains and fantasize about being the next Warren Buffet, the reality and less glamorous part of investing, and arguably the most important part, is trying to figure out what can go wrong and how to mitigate losses that can result. There is a lot to cover about risk and risk management, but today we will focus on one major risk related to market making: inventory risk. Here is what we’ll cover in today's article: - What is inventory value? - What is inventory risk? - How to mitigate inventory risk with Hummingbot And as always, you are welcome to join the #trader-chat on our Discord to discuss with the community how to improve your market making strategy. ## 1️⃣ What is Inventory risk?¶ As a market maker, your main role is to provide liquidity to other market participants. You are providing a service to other traders, offering to buy and sell assets from and to everyone else, while getting paid to do so through the spread size between your bid and ask offers (orders to buy low, sell high). To be able to provide this service, the market maker must hold some amount of assets in inventory in order to create orders and make trades, and this inventory has a value associated with it. ### Inventory Value As any market participant already knows, the prices of assets are constantly changing, and all traders must have a way to track if they are making profit or not. One simple way to track performance is to compare the total value of the assets owned by the trader. For example, let’s assume that you currently own 0.46820424 BTC and 14.6426 ETH: ### Day 1 Inventory 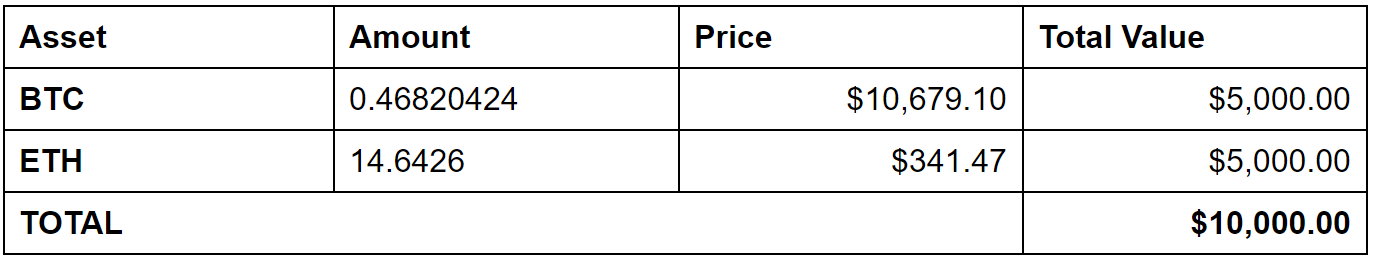 On the first day, the current value of your assets is $10,000. Even though you don't actually own any USD and only own BTC and ETH, you have the ability to convert your BTC and ETH to $10,000 at current market prices. Inventory value can fluctuate due to changes in market prices because the value of the assets relative to the benchmark asset can change If you haven’t traded (HODL!), on day 2 you would still have the same amount of BTC and ETH from the starting portfolio. ### Day 2 Inventory 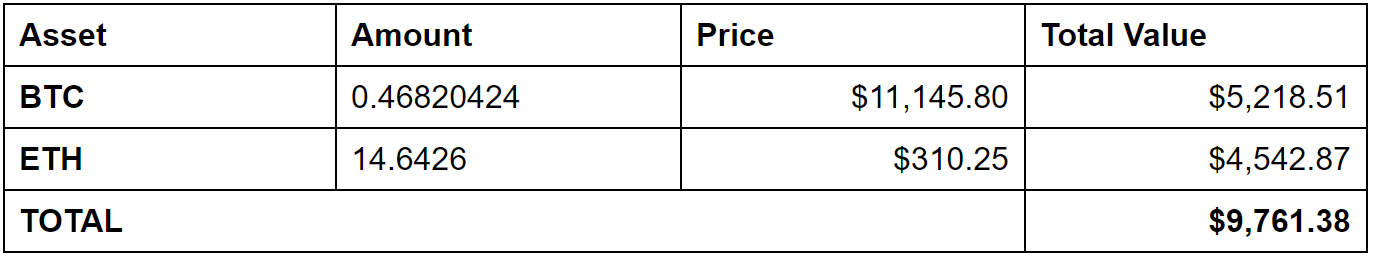 However, since the USD prices for these assets changed, the inventory value has gone down to $9,761.38. The BTC value went up, while the ETH value went down. Inventory value is the current value of all assets held in a portfolio, quantified to some chosen benchmark or reference asset (e.g. USD). Choosing the benchmark reference asset for determining value varies by investor. For example, investors from the U.S. may use USD, whereas an investor in Europe may choose Euro. This is because, at least currently, most of their costs (food, rent) are still denominated in USD (or Euro), and fiat is still the benchmark for their assets and buying power. ## 2️⃣ Inventory risk in trading The main objective of a market maker is to increase his total inventory value over time. The more common and general approach to investing is trying to buy assets that will appreciate in value in the future. This is “directional” investing, buying “cheap” assets and betting that the price of an asset will eventually go up. In contrast, a market maker tries to increase portfolio value over time by capturing incremental bid-ask spreads and accumulating them over time. The market maker continually offers to simultaneously buy and sell assets, offering to be at a slightly lower price than he is offering to sell. If the market maker is able to complete a buy and sell, they are able to capture some of this difference, the “bid-ask spread”. The more times a market-maker can complete this cycle of buy and sell, the more profits they are able to accumulate. As I mentioned in the first academy article, the ideal situation for a market maker is when the price is moving without a trend:  When prices are trading within a range, the more likely a market maker's buys and sells being filled with equal frequency, and the more likely the market maker is able to accumulate incremental profits. The trouble begins when the prices start to trend in one direction. For example, if the price starts to trend downward, his buy orders will start to be filled, but not the sell orders:  Source: Our community member @Christian Feldmann The consequence of this situation is that the market maker will begin to increase the inventory of the asset that is losing value, resulting in total inventory value decreasing over time. Eventually, the price could come back to a profitable level and the market maker would be able to sell his inventory at a profitable price. But the problem is that, if this situation persists and the price keeps dropping, all the market maker inventory will be locked on one side. At some point, the market maker will have to decide between stopping his operation and wait for better prices or start selling his inventory at a loss to keep his operation going. This similar to a retail store manager started to increase his inventory, buying more products from suppliers at better prices, but his customers aren't very interested in buying his products. Even though the market maker creates both buy and sell orders, there’s no guarantee that both sides will be filled. In the example above, the bids keep getting filled but the sells never get filled. This also exposes the market maker to the risk of swings in the amount of inventory held. For example, the market maker might accumulate assets losing value; conversely, the market maker might end up selling off assets that are appreciating in value. > Inventory risk is the probability a market maker can't find buyers for his inventory, resulting in the risk of holding more of an asset at exactly the wrong time, e.g. accumulating assets when prices are falling or selling too early when prices are rising. ## 3️⃣ Inventory risk management with hummingbot Inventory risk is the main risk of market making. That’s why Hummingbot allows a lot of strategy customization designed to mitigate inventory risk and why our team continues to work on even more features around this. This flexibility allows the market maker to mitigate his operational risks in a lot of different ways, and make adjustments that fit his major strategy. Here are a few examples on how the inventory risk can be controlled: ### History command The `history` command displays historical trades as well as a summary of changes in the total asset amounts since the bot started. It's a good way to visualize how much the inventory changed on each side, and compare with the total value. ### Inventory skew Using `config inventory_skew_enabled` the bot will change the `order_amount` on every new order, to rebalance the total inventory size. The target proportion of each asset on the inventory can be defined through the command `config inventory_target_base_pct` and how much the inventory can deviate from this proportion using `config inventory_range_multiplier`.  As can be seen above, there is more BTC than USDT on the inventory, and the bot is selling more than buying. This parameter can be used as inventory protection, for example, if the market maker spots a trend forming in one direction: if the BTC price is trending up, the market maker could start to accumulate more BTC, setting `config inventory_target_base_pct` to 70. Also, it is particularly useful, if you are trading a non-USD pair, (ETH-BTC for example), where the trader can evaluate the value of each asset paired with USD, and adjust the inventory skewness, if you think one of the assets will have a higher value in the future.  > Inventory skew is like an ongoing pendulum balancing act; once a trader accumulates more of one asset, Hummingbot adjusts order sizes (smaller buys, larger sells) to try to get back to the target holding amount, and vice versa. Inventory skew aims to minimize the risk of inventory amounts swinging around too much. Trying to maintain a target ratio such as 50% helps to ensure that the market maker can continue to quote both bid and ask sides and capture bid-ask spreads. ### Filled Order Delay Through the `filled_order_delay` parameter, the market maker is able to set a delay time for the bot to create subsequent new orders once a previous order has been filled. For example, with a `filled_order_delay` = 300 when an order created by the bot is filled, the next pair of orders will only be created 300 seconds later. This helps to manage periods when prices are trending. For example, in the diagram below, in a case when prices are trending down, bid orders keep getting filled once orders are refreshed.  If this is repeated and continues to go on, the market maker could quickly end up accumulating large amounts of the asset within a matter of just a few order refresh cycles. In the example above, the trader has bought assets 5 times. By introducing a delay between filled orders and placing new orders, this spaces out orders and dampens the potential accumulation of assets, allowing for some time for price trends to stabilize.  You can see above, since the bid order in period 1 was filled, the bot didn’t place orders in periods 2, 3, and 4. So in this downward price trend, the bot only bought twice (periods 1 and 5) whereas when filled order delay was not enabled, the bot would have bought in all five periods. ### Hanging Orders Hanging orders is a function that instructs Hummingbot to treat buys and corresponding sell orders created at the same time as a pairing. If one side gets filled, the bot keeps the other side of the pairing outstanding, creating the opportunity and possibility for that side to eventually get filled:  In the example above, the buy order for period 1 was filled. But since hanging orders mode was enabled, the original sell order from period 1 is not canceled during the refresh cycle (period 2) and remains outstanding. Meanwhile, the bot continues its operation of creating new orders (see periods 2 through 5). In the example, prices changed direction, and eventually at some point in the time, the hanging sell order was filled, around period 5. The benefit of this strategy is that it creates the possibility of the pairings to be “completed” and balanced. In the example above, hanging orders allow the trader to match the buy and sell eventually, while locking in the bid-ask spread. ### Ping Pong The ping pong strategy is another strategy that tries to keep buys and sells balanced. It does so by creating orders only on the opposite side of an order that has been filled. For example:  Because the buy order from period 1 was filled, the bot stops placing buy orders and only places sell orders (periods 2-4). Only when a sell order is eventually filled (period 4) will the bot resume creating both buy and sell orders (period 5). ### Adjust spread on one side to follow a price trend Usually, the market makers apply the same `bid_spread` and `ask_spread`. This is great on sideways markets, because the price will be moving inside a range, and naturally the inventory will tend to be at a 50/50 rate, and the market maker will profit from the spread. But like we said above, it gets problematic during a trending market, as the inventory may start to accumulate on the side of the less valuable asset. An option to mitigate this is to tighten the spread on one side, to increase the probability of those orders being filled first. Example: Mark, the market maker started his operations on the BTC-USDT with `bid_spread` = 0.5 and `ask_spread` = 0.5. But the price started trending up, so he changed his parameters to `bid_spread` = 0.1 and `ask_spread` = 0.9. That way, his total spread is still the same (1%), but his buy offers now have a higher chance to be filled before the sell offers. Scripts Hummingbot has a built-in script function, where you can create your own custom strategy, and the bot will adjust the parameters based on any strategy you want. All you need is know how to code on Python, create a .py file integrated with Humminbot code base, and activate the script through config script_enabled command (you can find more information about scripts here. You could even create a script that replicates an Automated Market Making logic, as this reddit user asked. Our developer team is working on a lot of improvements for the scripts module, because this is the main way Hummingbot users will be able to implement their customized strategies. ## 4️⃣ Wrapping up¶ Becoming a trader these days is really easy. But being a good trader, that’s another story. What I realized after these years studying financial markets is that the main thing that separates good traders from bad traders is how much they know about risk and how they manage it. A good strategy isn’t only about finding the best way to make money, but also about knowing what to do when the market moves against your plan. Understanding the risks associated with each type of trading operation is essential to finding a sustainable and profitable strategy. The major risk associated with market making is the inventory risk. Understanding and learning ways to mitigate it should be a priority for everyone looking to operate as a market maker on any market. This article covered an explanation about the topic, and some practical ways to manage this risk using hummingbot, but this is such an important topic that there is a huge amount of research papers about it, like Dealing with the Inventory Risk: A Solution to the Market Making Problem and Market making with asymmetric information and inventory risk, and eventually, we will talk more about this topic in a close future. Also, with the recent rise of the Automated Market Maker protocols (liquidity pools like Uniswap), liquidity mining, and everything related to Decentralized Finance (DeFi), it is really important to understand the risks if you are looking to be a passive market maker. So, stay tuned on our blog, because soon we will publish an article comparing what are the key differences between these protocols and the traditional order book market making. See you all next week. ## 5️⃣ Join our community If you want to learn more, make sure to follow our blog updates for new articles every week. While you wait for the next post, remember to join our Discord server, a place where our community talks about market making and arbitrage, and all the possible ways you can use Hummingbot to improve your trading strategies. Also, if there is any specific topic you want us to cover on the Hummingbot Academy, contact our team on Discord, or send an email to academy@hummingbot.io. See you soon, and I wish you all a profitable trading session! See you all next week!여기까진 Hummingbot 블로그에서 말하는 인벤토리 리스크와 관련된 글이었습니다. 다만 재고 리스크는 단순히 보유 자산 가치가 흔들리는 문제를 넘어, 전략의 지속 가능성과 포트폴리오 전체 성과를 좌우하는 핵심 요소입니다. 예를 들어, 스프레드 수익을 꾸준히 쌓고 있다고 해도, 한쪽으로 치우친 재고가 급격한 가격 변동으로 평가손실을 키운다면 전체 PnL은 쉽게 음수로 돌아설 수 있습니다.
-
정량적 지표 활용: 스프레드 수익과 가격 변동으로 인한 평가손익을 분리(PnL 분해)해, 수익이 스프레드 덕분인지 방향성 변동 때문인지 파악하세요.
-
동적 스프레드 조정: Avellaneda–Stoikov 같은 모델은 변동성·재고 수준에 따라 스프레드를 자동으로 조절하여, 재고 편향을 줄이고 예상치 못한 추세에 대응합니다. 이 내용은 다음 포스팅에서 이어서 할 예정입니다.
-
헤징과 제한 설정: 현물 마켓 메이킹 시 선물이나 옵션으로 반대 포지션을 잡아 위험을 상쇄하거나, 최대 보유량과 손실 한도를 사전에 정의해두면 재고가 갇히는 상황을 완화할 수 있습니다.
-
시장 환경 고려: 저유동성 코인이나 큰 뉴스 이벤트 직전에는 재고가 쉽게 묶일 수 있으므로, 변동성 지표(VIX, ATM IV)나 이벤트 캘린더를 참고해 포지션 규모를 조절하는 것이 좋습니다.
-
심리적 관리: 손실 상태에서 무리한 물타기를 피하고, 주기적으로 봇 성과를 검토하는 프로세스를 갖추면 장기적으로 안정성을 높일 수 있습니다.
마켓 메이킹의 본질은 단기적인 거래를 반복하며 작은 스프레드를 포착하는 것이지만, 재고 리스크를 통제하는 능력이야말로 장기적으로 시장에서 살아남는 힘이 됩니다. 꾸준히 데이터를 기록·분석하고, 시장 상황과 전략을 함께 점검해 나간다면 더욱 탄탄한 트레이딩 운영이 가능할 것입니다.
참고자료
- https://github.com/hummingbot/hummingbot
- https://hummingbot.org/blog/what-is-inventory-risk
