What is Arbitrage?
차익거래란 무엇인가요?

지난주 저희는 Hummingbot 아카데미의 첫 번째 글로 마켓 메이킹에 대한 소개를 다루었으며, 오늘은 다음 질문에 답하기 위해 차익거래(Arbitrage)에 대해 논의합니다:
- 차익거래란 무엇인가요?
- 차익거래자들은 무슨 일을 하나요?
- 차익거래는 어떻게 운영하나요?
- 나만의 차익거래 로봇은 어떻게 만드나요?
저희 Hummingbot 아카데미의 목표는 여러분이 마켓 메이킹과 차익거래에 대해 더 많이 배우고, 저희의 무료 오픈소스 로봇을 사용하여 자신만의 전략을 구현하는 방법을 돕는 것입니다.
✅ 차익거래가 무엇일까요?
차익거래의 개념은 매우 간단합니다:
차익거래는 시장 간의 자산 가격 차이로부터 이익을 얻기 위해 자산을 구매하고 판매하는 행위입니다.
차익거래가 정확히 어떻게 발생하는지 더 잘 설명하기 위해, 바나나에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다. 네, 바나나입니다.

경제의 상당 부분이 바나나 생산에 기반을 둔 작은 마을을 상상해 보세요. 많은 농장들이 현지 시장에서 자신들의 작물을 판매합니다.
이로 인해 현지에서 많은 바나나가 판매되고, 자연스럽게 높은 공급으로 인해 가격이 매우 저렴합니다. kg당 0.50달러라고 가정해 봅시다.
몇 킬로미터 떨어진 곳에는 큰 도시가 있지만, 그 경제는 대부분 산업에 기반을 두고 있어 주변에 바나나 농장이 많지 않습니다.
하지만 그 큰 도시의 시민들은 건강을 위해 여전히 과일을 먹고 싶어 하고, 이는 바나나에 대한 큰 수요를 만들어내며, 기꺼이 kg당 0.65달러를 지불하려고 합니다.
여기에 기회가 있다는 것이 꽤 명확하게 보입니다. 한 상인은 작은 마을에서 바나나를 사서 큰 도시에서 팔고, 운송된 킬로그램당 0.15달러(운송 비용 제외)의 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다.
이 경우 상인(차익거래자)은 차익거래를 하고 있는 것입니다: 한 시장에서 바나나(자산)를 사서 다른 시장으로 운송하여 이익을 남기고 팔면서, 거래의 양쪽이 동시에 체결되면 이익을 확정하여 위험을 줄입니다.
✅ 마켓 메이킹과 차익 거래는 같은 것 아닌가요?
마켓 메이킹과 차익 거래의 기본 개념은 낮은 가격에 사서 높은 가격에 팔아 작은 이윤을 남기는 것으로 매우 유사하지만, 핵심적인 차이점은 마켓 메이커와 차익거래자가 거래를 찾는 '장소'에 있습니다.
💡 전당포 주인과 같은 마켓 메이커는 단일 장소에서 운영하며, 동일한 시장에서 매수 및 매도 제안을 합니다. (도시 간에 상품을 운송하는 상인과 같은) 차익거래자는 하나 이상의 장소에서 운영하며, 두 개(또는 그 이상)의 다른 시장에서 매수 및 매도 제안을 가져옵니다.
각각이 시장에 미치는 영향도 다릅니다. 마켓 메이커는 유동성을 제공하고, 매수-매도 스프레드와 슬리피지를 줄이는 반면, 차익거래자는 두 시장(보통 유동성이 높은 시장과 낮은 시장)에서 유동성을 제거하지만, 두 장소의 가격이 같은 수준으로 수렴하도록 만듭니다.
✅ 시장 비효율성과 금융 시장에서의 차익거래
전 세계적으로 다양한 자산이 매일 거래되는 많은 다른 금융 시장이 있습니다.
모든 주요 도시나 국가는 보통 자체 금융 거래소를 가지고 있으며, 이곳에서 모든 종류의 투자자들이 만나 다양한 금융 상품을 사고팝니다.
뉴욕에는 나스닥(NASDAQ)과 뉴욕증권거래소(NYSE), 시카고에는 CME와 CBOE, 일본에는 JPX, 중국에는 SSE, 독일에는 FRA, 브라질에는 B3 등이 있으며, 이 목록은 계속됩니다.
그리고 정보 기술에 큰 발전이 있었음에도 불구하고, 수많은 거래소와 각 거래소 간의 거리는 여전히 소위 시장 비효율성(market inefficiencies)을 낳습니다.
이를 설명하기 위해, 두 다른 시장에서의 달러-엔(USD-JPY) 가격을 살펴보겠습니다.
어떤 시점에서 뉴욕과 일본 거래소의 오더북이 정확히 동일하다고 가정해 봅시다:
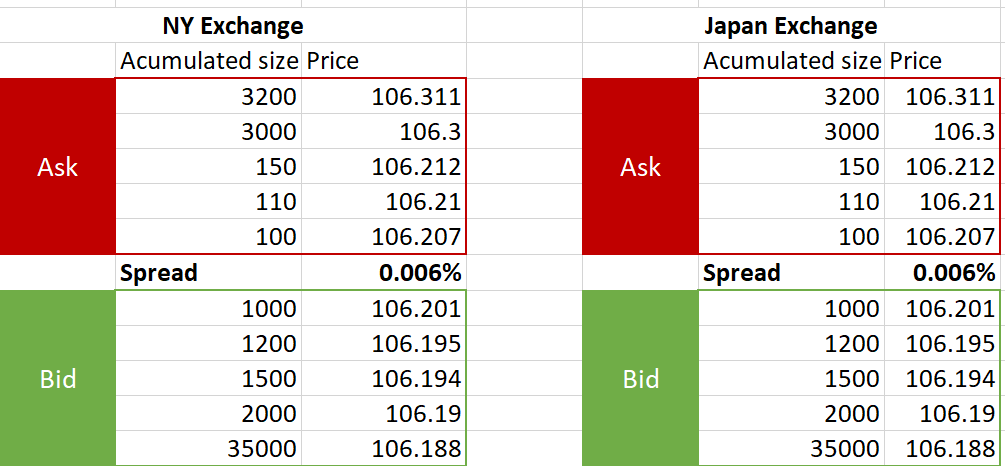
그때, 한 투자자가 일본 거래소에서 시장가로 360엔을 매수하는 주문을 보냅니다.
다음에 일어날 일은 일본 거래소 오더북에 새로운 매도 호가(Ask price)가 생기는 것이고, 보통 마켓 메이커들은 그 주문으로 인해 생긴 스프레드 격차를 메우기 위해 오더북에 새로운 매수 주문(Bid orders)을 생성할 것입니다:
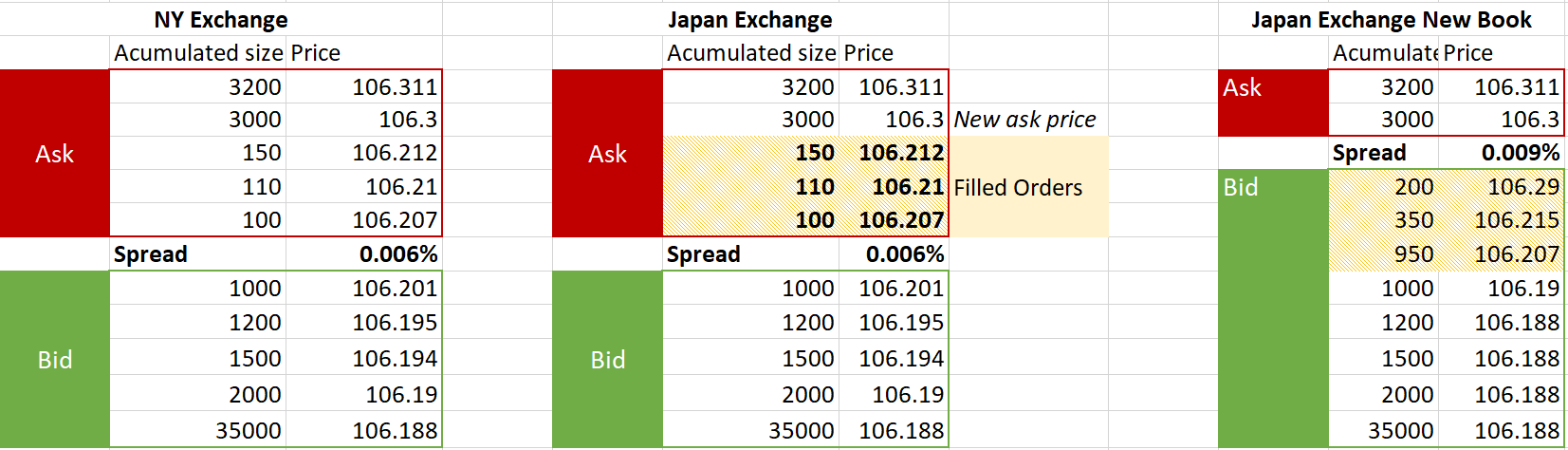
이때 차익거래자가 움직입니다. 뉴욕 거래소에서 106.207의 가격으로 100엔을 사고, 즉시 일본 거래소에서 106.29에 팔아, 거래에서 총 8.70달러(0.082%)의 이익을 얻습니다.
결국, 더 많은 차익거래가 발생함에 따라 뉴욕 거래소의 매도 호가는 일본 거래소의 매도 호가와 일치할 때까지 올라갈 것입니다.
💡 전통적인 금융 시장에서는 엄청난 양의 차익거래 경쟁이 있으며, 수익성은 밀리초(milliseconds) 단위로 결정됩니다. 이를 수행하는 회사들은 보통 차익거래 알고리즘의 속도를 높이기 위해 기술과 인프라에 막대한 투자(수십억 달러)를 합니다.
✅ 암호화폐와 차익거래 기회
지난 10년간 암호화폐 가치가 상승함에 따라 거래소 환경도 이 성장을 따라갔고, 오늘날 Coinmarketcap.com은 총 311개의 거래소에 6,974개의 다른 암호화폐가 거래될 수 있다고 목록에 올리고 있습니다.
이것은 모든 거래소에 걸쳐 다양한 거래량, 유동성, 스프레드가 존재하기 때문에 여전히 존재하는 큰 시장 비효율성으로 인해 엄청난 양의 차익거래 기회를 만들어냅니다.
하지만 암호화폐 거래 환경에는 가능성의 추가적인 층을 더하는 새롭고 흥미로운 요소가 있습니다: 탈중앙화 거래소입니다.
💡 중앙화 거래소 (CEX): 모든 자산이 거래소의 관리 하에 있으며, 사용자의 잔액은 거래소에 의해 통제됩니다. (e.g. 바이낸스, 바이비트, 업비트, 빗썸 등)
💡 탈중앙화 거래소 (DEX): 모든 자산이 소유자의 관리 하에 있으며, 거래소는 구매자와 판매자가 개인 지갑 간에 거래를 실행할 수 있는 방법으로 기능합니다. (e.g. 유니스왑, 팬페이크스왑 등)
CEX 모델은 전통적인 금융 시장에 이미 존재하는 것을 반영한 것이며, 이러한 검증된 서비스는 암호화폐 공간에서 매우 오랫동안 제공되어 왔습니다. 특히 대형 거래소들 사이에서는 이미 많은 차익거래 경쟁이 벌어지고 있으며, 시간이 지남에 따라 좋은 기회를 찾기가 점점 더 어려워지고 있습니다.
반면에, DEX의 개념은 비교적 새롭고, 다양한 모델과 분산화 수준을 가진 많은 프로젝트들이 개발되고 있습니다.
사실, 유니스왑(Uniswap)과 같은 AMM(자동화된 마켓 메이커) 탈중앙화 프로토콜은 실제로 차익거래자들이 내부 가격을 다른 외부 거래소와 일치시키도록 조정하는 데 의존합니다.
이것은 수익성 있는 차익거래를 위한 다양한 기회를 열어줍니다.
따라서 이러한 기회를 찾고 있다면, 오늘날 운영 중인 탈중앙화 거래소들을 꼭 확인해 보세요.
💡 보통 모든 거래소는 각 거래 작업에 수수료를 부과하므로, 차익거래 전략을 계획할 때 거래 실행 비용을 반드시 고려해야 합니다. DEX는 또한 고려해야 할 추가적인 비용 층을 제시하는데, 트랜잭션이 어떻게 처리되는지에 따라 블록체인 트랜잭션 수수료와 같은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다.
✅ 자동화된 거래와 차익거래
수익성 있는 차익거래를 완료하는 데에는 두 가지 핵심 요소가 있습니다:
- 수익성 있는 가격 불일치가 있는 두 시장을 찾기;
- 다른 사람보다 먼저 오더북에 있는 시장 제안을 가져오기.
이론적으로는 다른 거래소에서 자산 가격을 확인하고 주문 크기와 가격을 입력하여 거래를 체결하는 수동 프로세스를 통해 차익거래 기회를 활용하는 것이 가능합니다.
하지만 거래를 완료하기 위해 버튼을 클릭할 준비가 되었을 때쯤에는, 당신이 보고 있던 주문을 다른 사람이 이미 가져갔을 가능성이 높고, 거래는 더 이상 수익성이 없을 것입니다.
알고리즘 트레이드 로봇의 사용은 위에서 언급한 두 가지 요소를 실행할 수 있는 속도 때문에 오늘날 시장에서 차익거래의 필수적인 구성 요소가 되었습니다. 로봇은 끊임없이 수익성 있는 거래를 찾고 감지되는 즉시 실행합니다.
🐦 Hummingbot에서는
create명령어를 사용하여 차익거래 전략을 만들 수 있으며, 어떤 전략을 사용할지 물었을 때arbitrage를 입력하면 됩니다.
✅ 차익거래의 위험
차익거래의 개념은 정말 간단합니다: 한 시장에서 싸게 사서, 다른 시장에서 동시에 비싸게 파는 것입니다.
성공하면, 이 작업은 투자에 있어서 하나의 큰 위험인 변동성 위험(volatility risk)을 제거합니다.
차익거래자들은 가격 움직임에 대해 걱정하거나 시장 방향을 찾으려고 노력할 필요가 없으며, 한 곳에서 더 낮은 가격에 사서 다른 곳에서 즉시 더 높은 가격에 팔 수 있다는 것을 알 때만 거래할 것입니다.
하지만 모든 트레이딩 전략과 마찬가지로, 차익거래도 완전히 위험이 없는 것은 아닙니다.
위험의 대부분은 거래 실행(다른 사람보다 얼마나 빨리 거래를 체결할 수 있는지)과 시장 유동성(거래하려는 가격의 주문이 시장에 충분하지 않음)에 있습니다.바나나 상인을 생각해 보면, 한 도시에서 다른 도시로 이동하는 동안 문제(느린 트럭, 펑크 난 타이어 등)가 발생할 수 있으며, 그가 큰 도시에 도착했을 때 사람들이 지불하려던 가격이 낮아져 그의 이익이 줄어들거나 심지어 손실을 보고 거래를 마감할 수도 있습니다.
어느 정도까지, 차익거래자들은 실행 위험을 완화하고, 예를 들어 신뢰할 수 있는 인프라에 막대한 투자를 하거나, 거래소 서버에 더 가까이 운영을 옮기는 등의 이점을 만들 수 있습니다.
또한, 차익거래 경쟁이 치열해질수록 기회를 찾기가 점점 더 어려워집니다. 차익거래자들은 장기간 기회를 찾을 수 있지만, 그것을 찾을 것이라는 보장은 없습니다.
다른 모든 유형의 거래와 마찬가지로, 자산을 위험에 빠뜨리기 전에 위험을 이해하고 전략을 테스트해야 합니다.
🐦 Hummingbot에서는
paper_trading명령어를 사용하여 모의 투자 모드를 활성화할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 자본을 위험에 빠뜨릴 필요 없이 실시간 시뮬레이션 환경에서 전략을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
고려해야 할 또 다른 중요한 위험은 거래를 실행하는 장소와 관련이 있습니다:
-
중앙화 거래소 (CEX)는 당신의 자산을 보관하고 있으며, 어떤 이유로든(해킹, 사기 등) 자산에 대한 접근이 거부될 수 있으므로, 거래소의 평판과 보안 시스템을 반드시 조사해야 합니다.
-
탈중앙화 거래소 (DEX) 운영은 거래 흐름을 제어하기 위해 스마트 계약에 의존하며, 코드의 버그나 결함은 자금이 잠기거나 도난당하는 것과 같은 큰 문제로 이어질 수 있으므로, DEX 이면의 프로그램에 주요 결함이 없는지 이해하는 것이 중요합니다. 코드 언어를 이해하지 못하더라도, 웹에서 가능한 취약점에 대한 정보를 찾아보세요.
✅ 저희 커뮤니티에 참여하세요
이것으로 시장 비효율성을 활용하여 수익성 있는 거래를 찾는 정말 간단한 전략인 차익거래에 대한 소개를 마칩니다. 다음 주에는 마켓 메이킹과 차익거래의 혼합인 교차 거래소 마켓 메이킹(Cross-exchange market making)을 다룰 것입니다.
더 배우고 싶다면, 매주 새로운 글이 올라오는 저희 블로그 업데이트를 꼭 팔로우하세요.
다음 글을 기다리는 동안, 저희 디스코드 서버에 참여하는 것을 잊지 마세요. 이곳은 우리 커뮤니티가 마켓 메이킹과 차익거래, 그리고 Hummingbot을 사용하여 트레이딩 전략을 개선할 수 있는 모든 가능한 방법에 대해 이야기하는 곳입니다.
또한, Hummingbot 아카데미에서 다루었으면 하는 특정 주제가 있다면, 디스코드에서 저희 팀에 연락하거나 academy@hummingbot.io로 이메일을 보내주세요.
곧 뵙겠습니다. 모두 수익성 있는 트레이딩 세션이 되시기를 바랍니다!
Show original (English)
 # Welcome to Hummingbot Academy! Last week we published the [first article](/_posts/2025-09-18-hummingbot-what-is-market-making.md) of the Hummingbot Academy, covering an introduction to what is Market Making, and today we discuss Arbitrage in order to answer the following questions: - What is arbitrage? - What do arbitrageurs do? - How to run arbitrage operations? - How do I create my arbitrage robot? Here at Hummingbot Academy our goal is to help you learn more about market making and arbitrage, and how to use our free open-source robot to implement your own strategy. ## But what is arbitrage? The concept of arbitrage is pretty simple: > **Arbitrage** is the purchase and sale of an asset in order to profit from a difference in the asset's price between markets. To better explain exactly how an arbitrage operation happens, let's talk about bananas. Yes, bananas.  Picture a small town, where a big part of its economy is based on bananas production, with a lot of farms selling their crop on the local market. This result in a lot of bananas being sold locally, and naturally due to the high offer, they are pretty cheap to buy, let's say for $0.50/kg. A few kilometers away lies a big city, but most of its economy is based on industry, therefore there aren't many banana farms surrounding it. But citizens of that big city still want to eat fruit to have good health, which creates a big demand for bananas, and they are willing to pay $0.65/kg. It's pretty clear to see there is an opportunity here, and a merchant could buy bananas from the small town, sell on the big city, and profit $0.15 (without accounting the transportation costs) for each transported kilogram. The merchant (arbitrageur) in this case is doing an arbitrage operation: buying and transporting bananas (the asset) from one market and selling it on another market for a profit, while reducing his risk by locking his profits if both sides of the deal are closed at the same time. ## Isn't it the same as a market making operation? Although the basic concept of both operations is pretty similar (buy low and sell high with a small profit margin), the key difference is the 'where' the market maker and the arbitrageur look for deals. > 💡 The market maker **like a pawnshop owner** operates on a single place, making buy and sell offers on the same market. The arbitrageur (like a merchant transporting goods between towns), operates on more than one place, taking buy and sell offers from two (or more) different markets. The way each one affects the markets is also different because while a market maker is providing liquidity, reducing bid-ask spread and slippage, while the arbitrageur is removing liquidity from two markets (usually from a high-liquidity market and a low-liquidity market), but pushing the prices to converge on the same level on both places. ## Markets inefficiencies and arbitrage on financial markets Around the world, there are a lot of different financial markets where a variety of assets are being traded on a daily basis. Every major city or country usually has its own financial exchange were all kind of investors meet to buy and sell different financial instruments. We have NASDAQ and NYSE on New York, CME and CBOE on Chicago, JPX on Japan, SSE on China, FRA in Germany, B3 in Brazil, and the list goes on and on. And even though there was a huge evolution in the information technology, the sheer amount of exchanges and the distance between each one still leads to so-called market inefficiencies. To illustrate this, we will take a look at the Dollar-Yen (USD-JPY) prices on two different markets. Let's assume that at some point in time, the order book of a New York and a Japan exchanges are exactly the same:  Then, an investor decides to send a order to buy 360 JPY on the Japan Exchange at market price. What will happen next is that there will be a new Ask price on the Japan Exchange book, and usually, the Market Makers will create new Bid orders on the book to fill the spread gap that was created by that order:  This is when the arbitrageur makes his move, buying 100 JPY at the New York exchange at the price 106.207 and selling them immediately on the Japan Exchange for 106.29, netting a total profit of 8.70 USD (0.082%) on the trade. Eventually, as more arbitrage operations happen, the Ask price on the NY exchange will go up until it matches the Ask price on the Japan Exchange. > 💡 In the traditional financial markets, there is a huge amount of arbitrage competition, with profitability being determined by milliseconds. The companies doing it usually make big investments (billions of dollars) in technology and infrastructure to increase the speed of arbitrage algorithms. ## Cryptocurrencies and arbitrage opportunities With the rise of cryptocurrencies value over the last 10 years, the exchanges landscape followed this growth, and today [Coinmarketcap.com](coinmarketcap.com) lists a total of 311 exchanges where 6,974 different cryptocurrencies can be traded. This creates a huge amount of opportunities for arbitrage operations, due to the big market inefficiency that still exists between all these exchanges with a wide range of volume, liquidity, and spread across all of them. But there is a new and interesting factor in the cryptocurrency trading environment that adds an extra layer of possibilities: decentralized exchanges. > 💡 **Centralized Exchange (CEX)**: All the assets in the custody of the exchange, and the user's balance is controlled by the exchange. > 💡 **Decentralized Exchange (DEX)**: All the assets are in the custody of their owners, and the exchange function as a way for buyers and sellers to execute a trade between their private wallets. The CEX model is a reflection of what already exists in the traditional financial markets and this kind of tried-and-true service has been offered in the cryptocurrency space for a very long time. We can say that there is already a lot of competition doing arbitrage operations, especially among the bigger exchanges, and as time goes by, it is getting harder to find good opportunities. On the other hand, the concept of a DEX is relatively new and there are a lot of projects with different models and levels of decentralization being developed. As a matter of fact, AMM (Automated Market Makers) decentralized protocols like Uniswap actually rely on arbitrageurs to adjust their internal prices to match other external exchanges. This opens up a wide array of opportunities for profitable arbitrage. So, if you are looking for these opportunities, be sure to check the of the decentralized exchanges that are operational today. > 💡 Usually, all exchanges charge a fee on each trade operation, so be sure to consider the cost of executing the trade when planning your arbitrage strategy. DEXes also present an extra layer of cost to be considered, because depending on how the transactions are processed, there might be some added cost like blockchain transaction fees. ## Automated trade and arbitrage There are two key components on completing a profitable arbitrage trade: - Find two markets with profitable price discrepancies; - Take the market offers listed on the book before anyone else. In theory, it is possible to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities through the manual process of checking the price of an asset across different exchanges and type your order size and price to close the deal. But by the time you are ready to click the button to complete the trade, it is most likely that another person already took the order you were looking at, and the trade won't be profitable anymore. The use of algorithmic trade robots has become an essential component of arbitrage operations in today's markets because of the speed it can execute both components listed above, by constantly looking for profitable trades and executing them at the exact moment they are detected. > 🐦 You can create an arbitrage strategy on Hummingbot using the create command and then typing arbitrage when asked what is the strategy you want to use. ## The risks of arbitrage The concept of arbitrage operations is really simple: buy low on one market, sell high on another at the same time. When successful, this operation eliminates one big risk when it comes to investing: volatility risk. Arbitrageurs don't have to worry about the price movements or try to find the market direction, and they will only trade if they know they can buy in one place at a lower price and immediately sell it at another place at a higher price. But as it happens with all trading strategies, arbitrage isn't completely risk-free. The majority of the risk lies upon the trade execution (how fast can you close the trade before someone else) and the market liquidity (not enough orders available on the markets with the price you are looking to trade). If you think about the banana's merchant, he could have problems while traveling from one city to another (slow truck, flat tire, etc), and by the time he reaches the big city, the price people were willing to pay could be lower, reducing his profits or even close the trade at a loss. To some degree, arbitrageurs can mitigate the execution risk and create some advantages, for example by investing heavily in reliable infrastructure, or moving his operation closer to the exchange servers. Also, as arbitrage gets increasingly competitive, opportunities become increasingly hard to come by. Arbitrageurs may search for opportunities for long periods of time but are not guaranteed to find them. As with any other type of trade, be sure to understand the risks and test your strategy before putting your assets at risk. > 🐦 With Hummingbot you can enable the paper trading mode using the command paper_trading, which allows you to test your strategy in a real-time simulated environment, without the need to put your capital at risk. Another important risk you must consider is related to where you are executing your trades: - Central Exchanges have the custody of your assets, and your access to them can be denied for any reason (hacks, scams, etc), so be sure to research the exchange reputation and security systems; - Decentralized Exchanges operations rely on the smart contracts to control the trade flow and bugs or flaws on the code can lead to big problems like funds being locked or stolen, therefore it is important to understand the if the program behind the DEX doesn't have major flaws. Even if you don't understand the code language, look around the web for information about possible vulnerabilities. ## Join our community And this concludes our introduction to arbitrage, a really simple strategy that take advantage of market inefficiencies to find profitable trades. Next week we will cover Cross-exchange market making, which is a mix of market making and arbitrage. If you want to learn more, make sure to follow our blog updates for new articles every week. While you wait for the next post, remember to join our Discord server, a place where our community talks about market making and arbitrage, and all the possible ways you can use Hummingbot to improve your trading strategies. Also, if there is any specific topic you want us to cover on the Hummingbot Academy, contact our team on Discord, or send an email to academy@hummingbot.io. See you soon, and I wish you all a profitable trading session!참고자료
- https://github.com/hummingbot/hummingbot
- https://hummingbot.org/blog/what-is-arbitrage
